Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Dan Robinson and Eric McFadden for the following tips:
The Biden Choice on USAGM: Business as usual, or major change (USC Center on Public Diplomancy)
Several years ago, I wrote about ongoing problems at Voice of America and its parent agency, which re-branded in 2018 as the U.S. Agency for Global Media (USAGM), and how Donald Trump would deal with them.
I suggested that the Voice of America could be shut down with little impact on the global media scene. This sparked outrage in some quarters, especially from those invested in perpetuating the yearly $600 million to $800 million taxpayer-funded media structure aimed at foreign audiences.
Space limitations prohibit a thorough review of events since Donald Trump’s nominee to head USAGM, Michael Pack, finally achieved Senate confirmation and took up his post after being blocked for two years by Democrats and some anti-Trump Republicans.
Pack faced a wave of hit pieces by major anti-Trump media as he moved to gain control of the bloated and entrenched USAGM bureaucracy, confront security issues at USAGM, and tackle political bias at VOA. His removal of key officials in charge of USAGM networks is still being fought out in the courts.[…]
Trump Appointee Unconstitutionally Interfered With VOA, Judge Rules (NPR)
The chief executive over the Voice of America and its sister networks has acted unconstitutionally in investigating what he claimed was a deep-seated bias against President Trump by his own journalists, a federal judge has ruled.
Citing the journalists’ First Amendment protections, U.S. Judge Beryl Howell on Friday evening ordered U.S. Agency for Global Media CEO Michael Pack to stop interfering in the news service’s news coverage and editorial personnel matters. She struck a deep blow at Pack’s authority to continue to force the news agency to cover the president more sympathetically.
Actions by Pack and his aides have likely “violated and continue to violate [journalists’] First Amendment rights because, among other unconstitutional effects, they result in self-censorship and the chilling of First Amendment expression,” Howell wrote in her opinion. “These current and unanticipated harms are sufficient to demonstrate irreparable harm.”[…]
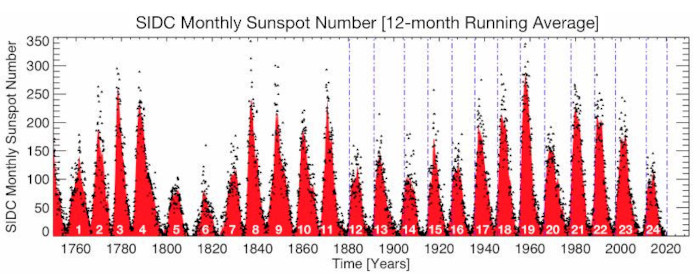
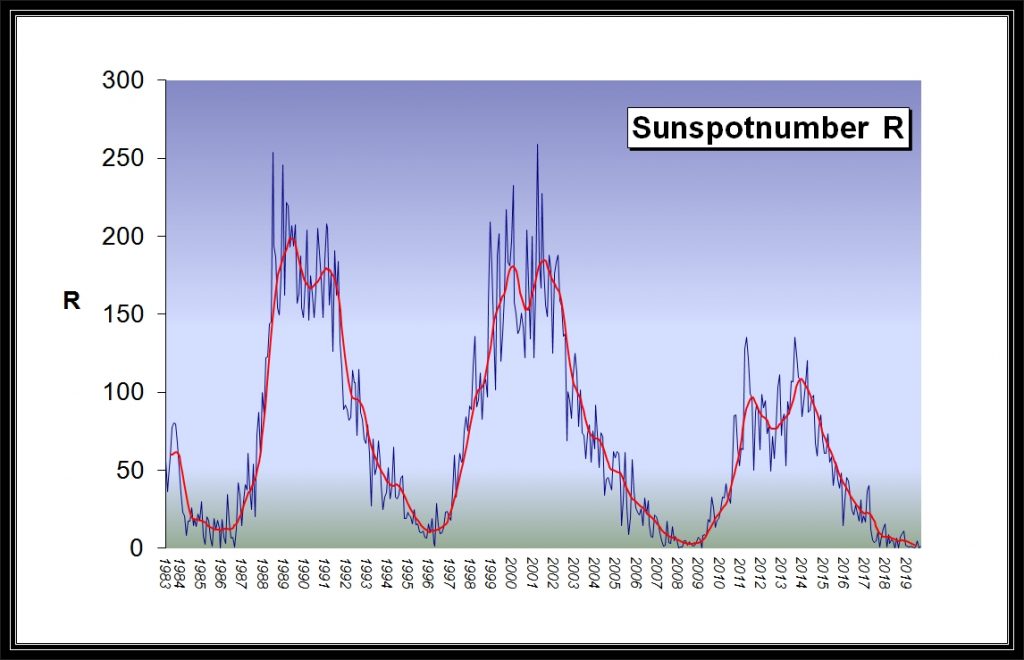
Sunspot Cycle 25 could be among the strongest ever (Southgate ARC)
The ARRL reports a research paper has concluded that Solar Cycle 25 will stronger than the just-ended Solar Cycle 24 and likely stronger than Solar Cycle 23
The League says:
A research paper, “Overlapping Magnetic Activity Cycles and the Sunspot Number: Forecasting Sunspot Cycle 25 Amplitude,” by Scott W. McIntosh, Deputy Director of the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, et al., has concluded that Solar Cycle 25 could be among the strongest sunspot cycles ever observed, and will almost certainly be stronger than the just-ended Solar Cycle 24 (sunspot number of 116). The scientists say it will also most likely be stronger than Solar Cycle 23 (sunspot number of 180). As the abstract explains:
“The sun exhibits a well-observed modulation in the number of spots on its disk over a period of about 11 years. From the dawn of modern observational astronomy, sunspots have presented a challenge to understanding — their quasi-periodic variation in number, first noted 175 years ago, stimulates community-wide interest to this day. A large number of techniques are able to explain the temporal landmarks, (geometric) shape, and amplitude of sunspot ‘cycles;’ however, forecasting these features accurately in advance remains elusive.
“Recent observationally motivated studies have illustrated a relationship between the sun’s 22-year magnetic cycle and the production of the sunspot cycle landmarks and patterns, but not the amplitude of the sunspot cycle. Using (discrete) Hilbert transforms on more than 270 years of (monthly) sunspot numbers, we robustly identify the so-called ‘termination’ events that mark the end of the previous 11-year sunspot cycle, the enhancement/acceleration of the present cycle, and the end of 22-year magnetic activity cycles. Using these, we extract a relationship between the temporal spacing of terminators and the magnitude of sunspot cycles.
“Given this relationship and our prediction of a terminator event in 2020, we deduce that Sunspot Cycle 25 could have a magnitude that rivals the top few since records began. This outcome would be in stark contrast to the community consensus estimate of Sunspot Cycle 25 magnitude.”
McIntosh’s recorded presentation of the paper is available at this link
Use passcode z7qCn@3GThe research paper is at
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.15263.pdfSource ARRL Letter November 19, 2020
http://www.arrl.org/arrlletter
DEF CON ham radio talks on YouTube (Southgate ARC)
Talks from the DEF CON event are available on YouTube, they include a number of amateur radio talks from the conference’s Ham Radio Village
Among the amateur radio talks are:
• Talking to Satellites by Eric Escobar KJ6OHH
• The K0BAK News Van by Pete Kobak K0BAK
• Single Board Computers (Raspberry Pi) In Amateur Radio by Typer Gardner KI7ODK
• Ham Radio Snail Mail NTS and the Radiogram Format by Aaron Hulett K8AMH
• Hunting tape measure yagis and offset attenuators by Mark Smith KR6ZY
• APRS Demo by Bryan Lamoreaux KG7OOWHam Radio Village Playlist
Click hereOther DEF CON videos are at
https://www.youtube.com/user/DEFCONConference/videosoo
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!