 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Fred Waterer, for sharing this article highlighting unusual activity from Russia’s shortwave station UVB-76, sometimes known among shortwave listeners as “The Buzzer.” Known for its continuous buzzing and occasional coded voice messages, the station recently broke pattern by playing music–including Tchaikovsky’s Swan Lake–and transmitting atypical sounds alongside cryptic codes, sparking speculation about the source and meaning of the broadcast.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Fred Waterer, for sharing this article highlighting unusual activity from Russia’s shortwave station UVB-76, sometimes known among shortwave listeners as “The Buzzer.” Known for its continuous buzzing and occasional coded voice messages, the station recently broke pattern by playing music–including Tchaikovsky’s Swan Lake–and transmitting atypical sounds alongside cryptic codes, sparking speculation about the source and meaning of the broadcast.
Tag Archives: UVB-76
BBC Newshour Reports Jamming of UVB-76 (The Buzzer) With Music and Digital Imagery
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Mark, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Mark, who writes:
Thomas,
The morning (EST) edition of BBC Newshour on Wednesday presented a five-minute report on the jamming of Russian shortwave mystery station UVB-76 (The Buzzer) with music and digital imagery.
Newshour – Uncertainty over Russian ‘de-escalation’ near Ukraine – BBC Sounds
https://www.bbc.co.uk/sounds/play/w172xv5lss6rtdm
Report begins at 37:26
Also at:
BBC World Service – Newshour – Available now
https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p002vsnk/episodes/player
Sincerely,
Mark
Thank you for the tip, Mark. Impressive that this bit of shortwave news would be included in a Newshour report. They did a fantastic job including some audio clips from the Conet Project and authentic UVB-76 audio.
Radio Waves: Data RX via Web SDRs, Mystery Signals from Space, Public Media’s role in Democracy, and Pirates SPAM UVB-76
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Marty, Troy Riedel, and Rich Cuff for the following tips:
Receiving data with web based shortwave radios (Nuts and Volts)
Your computer and the Internet give you free access to over 100 web based shortwave receivers that you can use as if they were your own. Unfortunately, employing these radios to decode data transmissions can be very difficult or impossible — unless you know the secret.
[…]A while back, I discussed how to receive data signals with a low cost shortwave radio (N&V May 2015). Now, the concept takes on a new dimension since we are using virtual radios not in our possession.
As astonishing as it seems, many of these Web based shortwave receiver data signals can be processed and decoded using just your PC and some free decoding software. Yes, some signals are encrypted, and can’t be decoded. Fortunately, there are plenty of unencrypted data signals around to keep us busy for a long time.
However, as will be discussed later on, it does require a special trick to allow you to pipe the streaming audio signals from the Web to the decoding software. In this article, I will show you how to use these Web based shortwave receivers to access data transmissions and to get started in this exciting hobby. [Click here to read the full article…]
Unknown objects at the heart of the Milky Way are beaming radio signals, then mysteriously disappearing (Business Insider)
Ziteng Wang found a needle in an astronomical haystack.
Wang, a physics PhD student at the University of Sydney, was combing through data from Australia’s ASKAP radio telescope in late 2020. His research team had detected 2 million objects with the telescope and was classifying each one.
The computer identified most of the stars, and the stage of life or death they were in. It picked out telltale signs of a pulsar (a rapidly rotating dead star), for example, or a supernova explosion. But one object in the center of our galaxy stumped the computer and the researchers.
The object emitted powerful radio waves throughout 2020 — six signals over nine months. Its irregular pattern and polarized radio emissions didn’t look like anything the researchers had seen before.
Even stranger, they couldn’t find the object in X-ray, visible, or infrared light. They lost the radio signal, too, despite listening for months with two different radio telescopes. [Continue reading…]
Do countries with better-funded public media also have healthier democracies? Of course they do (Nieman Lab)
But the direction of causality is tricky. Do a democracy’s flaws lead it to starve public media, or does starving public media lead to a democracy’s flaws?
There’s a new book coming out in the U.K. this week called The BBC: A People’s History, by David Hendy. Its publisher calls it a “monumental work of popular history, making the case that the Beeb is as much of a national treasure as the NHS…a now global institution that defines Britain and created modern broadcasting.”
Cross the pond: While Americans generally like PBS and NPR, I wouldn’t expect them to come up quickly if you asked someone on the street to begin listing national treasures. (I’m even more sure America’s health care system would go unmentioned, too.) Who “created modern broadcasting” in the U.S.? It certainly wasn’t the two public broadcasters that didn’t hit airwaves until 1970. And what TV network is a “global institution” that “defines” the United States abroad? Apologies to PBS Newshour, but that’s CNN.
No one says “Auntie Peebs.”
It’s obvious that the U.S. approached the new broadcasting technologies of the 20th century in ways wildly different from their European peers — and in ways that reflect on the countries themselves. American radio began wild and unregulated, experimental, a bubbling font of creativity — and then quickly became commercialized, optimized for mass audiences and massive profits. The BBC, which turns 100 this year, was more structured, more statist, more controlled — but has remained more central to residents’ lives, more civic-minded, and more beloved. [Continue reading…]
Pirates Spammed an Infamous Soviet Short-wave Radio Station with Memes (Vice)
The UVB-76 numbers station took a break from being a suspected communications tool of Russian intelligence to blast ‘Gangnam Style’
Pirates hijacked an infamous short-wave radio station, which dates from the Soviet era but is still online today, and used it to broadcast everything from Gangnam Style to audio that draws memes when inspected under a spectrum analyzer.
For decades the numbers station known as UVB-76 has emitted an enigmatic series of beeps and a voice reading numbers and names, in what people suspect is a long running communications method for Russian intelligence. Since the broadcast is public, pirates are able to use their software-defined radio (SDR) transmitters to effectively flood the frequencies with noise and memes.
The recent barrage of attacks on the station come as Russia prepares to invade neighbouring Ukraine, where radio enthusiasts speculate at least some of the pirate broadcasts originate. [Continue reading…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
Radio Waves: Narco-Antennas, Pirate Radio Beginnings, Arqiva Restructure and Redundancies, and the Ghostly Buzzer
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Skip Arey, David Goren, Paul Evans, Kanwar Sandhu and Dave Porter for the following tips:
Special Report: Drug cartel ‘narco-antennas’ make life dangerous for Mexico’s cell tower repairmen (Reuters)
MEXICO CITY (Reuters) – The young technician shut off the electricity at a cellular tower in rural Mexico to begin some routine maintenance.
Within 10 minutes, he had company: three armed men dressed in fatigues emblazoned with the logo of a major drug cartel.
The traffickers had a particular interest in that tower, owned by Boston-based American Tower Corp (AMT.N), which rents space to carriers on its thousands of cellular sites in Mexico. The cartel had installed its own antennas on the structure to support their two-way radios, but the contractor had unwittingly blacked out the shadowy network.
The visitors let him off with a warning.
“I was so nervous… Seeing them armed in front of you, you don’t know how to react,” the worker told Reuters, recalling the 2018 encounter. “Little by little, you learn how to coexist with them, how to address them, how to make them see that you don’t represent a threat.”
The contractor had disrupted a small link in a vast criminal network that spans much of Mexico. In addition to high-end encrypted cell phones and popular messaging apps, traffickers still rely heavily on two-way radios like the ones police and firefighters use to coordinate their teams on the ground, six law enforcement experts on both sides of the border told Reuters.[…]
How Pirate Radio Rocked the 1960s Airwaves and Still Exists Today (HowStuffWorks)
If you’ve been binge-watching movies lately, you may have come across “Pirate Radio.” Director Richard Curtis’ 2009 comedy-drama stars the late Philip Seymour Hoffman as The Count, a disc jockey for an unlicensed rock radio station that broadcast from a rusty, decrepit ship off the British coast in the mid-1960s, defying government authorities to spin the rock records that weren’t allowed on the BBC at the time. The plot is based loosely on the saga of an actual former pirate station, Radio Caroline, that was founded by an offbeat Irish entrepreneur named Ronan O’Rahilly, the inspiration for the character portrayed by Bill Nighy.
“Pirate Radio” is a period piece, set in a time when the Rolling Stones’ “Let’s Spend the Night Together” and the Who’s “My Generation” were still scandalous and controversial rather than nostalgic anthems for today’s aging baby boomers. So you couldn’t be blamed for assuming that it depicts a long-vanished phenomenon, like Nehru jackets with iridescent scarves and psychedelic-patterned paper mini dresses.
To the contrary, though, more than a half-century later, pirate radio is still a thing. In fact, it’s possibly more widespread than it was in the 1960s, even in an age when streaming internet services such as Spotify and Pandora put the equivalent of a jukebox in the pocket of everyone with a smartphone. And as a bonus, Radio Caroline still exists — though, ironically, it’s gone legal.[…]
Arqiva confirms restructure and redundancies (IBC.org)
[Note: Arqiva is the UK domestic broadcast transmission provider.]
Arqiva is working on a restructure of its business that could result in a third of its staff being made redundant.
According to a report in the Telegraph, the media infrastructure business is preparing to cut around 500 staff, which is approximately a third of its workforce.
An Arqiva spokesperson confirmed to IBC365 that some job losses will occur.
They said: “The sale of our telecoms business makes Arqiva a smaller organisation, changes our revenue profile and reduces our available profit pool.
”We are therefore conducting a review of the costs and systems we need to run our business over the next three years.
”Regrettably, we will need to reduce the size of our workforce, but it’s much too early to speculate about numbers.”
The Telegraph report cites the shift to streaming and a drop in income for broadcasters as reasons for the potential cuts.[…]
The ghostly radio station that no one claims to run (BBC Future)
In the middle of a Russian swampland, not far from the city of St Petersburg, is a rectangular iron gate. Beyond its rusted bars is a collection of radio towers, abandoned buildings and power lines bordered by a dry-stone wall. This sinister location is the focus of a mystery which stretches back to the height of the Cold War.
It is thought to be the headquarters of a radio station, “MDZhB”, that no-one has ever claimed to run. Twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, for the last three-and-a-half decades, it’s been broadcasting a dull, monotonous tone. Every few seconds it’s joined by a second sound, like some ghostly ship sounding its foghorn. Then the drone continues.
Once or twice a week, a man or woman will read out some words in Russian, such as “dinghy” or “farming specialist”. And that’s it. Anyone, anywhere in the world can listen in, simply by tuning a radio to the frequency 4625 kHz.
It’s so enigmatic, it’s as if it was designed with conspiracy theorists in mind. Today the station has an online following numbering in the tens of thousands, who know it affectionately as “the Buzzer”. It joins two similar mystery stations, “the Pip” and the “Squeaky Wheel”. As their fans readily admit themselves, they have absolutely no idea what they are listening to.[…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
Radio Waves: Capitol Code, Clay’s Corner, The Buzzer, iHeart Layoffs, and Australian Hams
 Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors, William Lee, Stana Horzepa, Rich Cuff, and Marty for the following tips:
Capitol Records Building Morse Code (WA1LOU)
This iconic Los Angeles landmark has been emitting secret messages since it opened. However, only those with a keen eye for Morse code can decipher what they say.
It was the former president of Capitol Records, Alan Livingston, who got the idea to have the light on top of the building send out a signal in Morse code. The word chosen for this secret message was “Hollywood.” When the building opened in 1956, Samuel Morse’s granddaughter Leila Morse had the honor of turning the light on.
Read the rest of the story at Atlas Obscura.
Clay’s Corner February 2020 Edition (Northwest Broadcasters)
Some are interpreting this as meaning that – every – AM will be switching to digital leaving a Jillion AM only receivers with nothing to listen to (except for electrical gizmo noise). I give more credit than that to the owners of AM Radio Stations. I would highly doubt if any market would see all of their AM’s go digital. Perhaps in an ownership that had two AM’s it might make sense to have one of each.
[…]Other question is, what will the company that owns HD Radio (EXPERI) want to extract from the owner of an AM station that’s willing to put everything on the line and go all digital?
The bottom line is there appears to be a lot of interest in this proposal. The FCC’s process will likely draw a number of comments, pro and con. This will be an interesting process to watch. I can say one thing, never did I ever dream that we would be debating this issue![…]
Seven mysterious sounds science has yet to solve (Popular Science)
The Buzzer
Numbers stations—shortwave radio transmissions of monotone coded messages—are inherently creepy. But call sign UVB-76 has outcreeped them all by playing the same jolting tone from Russia since 1982. Similar broadcasts are useful for sending messages where snoops might intercept digital comms, so “the Buzzer” could simply assist spies. But it plays far fewer words and digits than confirmed espionage outlets, so some suspect it’s a science project that bounces radio waves off the ionosphere to detect solar flares. The most intriguing theory posits that it’s a doomsday device that will go silent should Russia suffer a nuclear attack, thus triggering retaliation.
My theory is that these mysterious sounds are actually the intro to a Pink Floyd song, possibly from their 1969 album Ummagumma. Because the early Floyd albums, before Dark Side of the Moon, are no longer heard on-air, the Russians stole this music knowing we’d never notice. Ooh, gotta go… I hear the black helicopters coming…[…]
iHeartMedia laid off hundreds of radio DJs. Executives blame AI. DJs blame the executives. (Washington Post)
When iHeartMedia announced this month it would fire hundreds of workers across the country, the radio conglomerate said the restructuring was critical to take advantage of its “significant investments … in technology and artificial intelligence.” In a companywide email, chief executive Bob Pittman said the “employee dislocation” was “the unfortunate price we pay to modernize the company.”
But laid-off employees like D’Edwin “Big Kosh” Walton, who made $12 an hour as an on-air personality for the Columbus, Ohio, hip-hop station 106.7 the Beat, don’t buy it. Walton doesn’t blame the cuts on a computer; he blames them on the company’s top executives, whose “coldblooded, calculated move” cost people their jobs.[…]
Amateur radio skills prove useful during bushfire emergencies (ABC News)
Amateur radio enthusiasts have proved themselves useful during the recent bushfires after traditional telecommunication channels broke down.
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is a skill and international hobby whereby enthusiasts use specific radio frequencies to communicate with each other.
In Australia, users must complete an exam to obtain a license through the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA).
It was volunteers with these skills who were called in to assist during the recent New South Wales bushfires.
Neil Fallshaw is vice-president of WICEN NSW Communications, a group of volunteers with amateur radio licenses who can help in emergency situations.
He said about 30 members provided a temporary radio system in the Bega, Cobargo, Narooma, and Bermagui areas after some of the local radio infrastructure was damaged or had lost power.
“We deployed one of our radio repeaters on the mountains. We put a radio repeater system on that mountain to cover a portion of the south coast,” Mr Fallshaw said.
He said that radio system assisted the NSW Volunteer Rescue Association and Bega Valley Shire Council staff to communicate from bushfire-affected towns like Bermagui and Cobargo.
“They normally use just mobile phones, but the mobile phones in the area were down because of fire damage,” Mr Fallshaw said.[…]
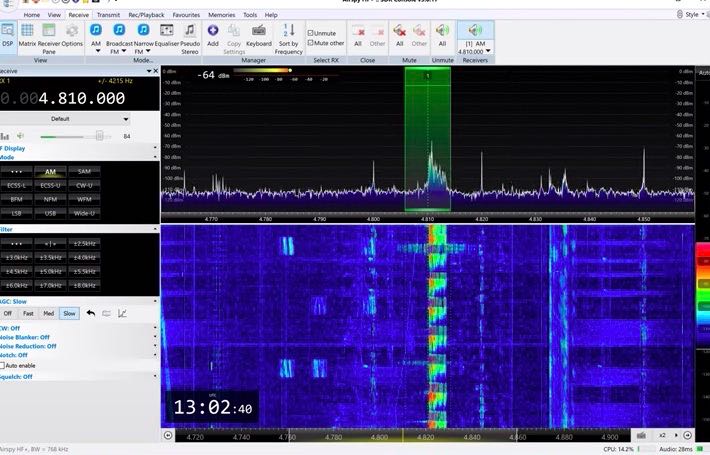
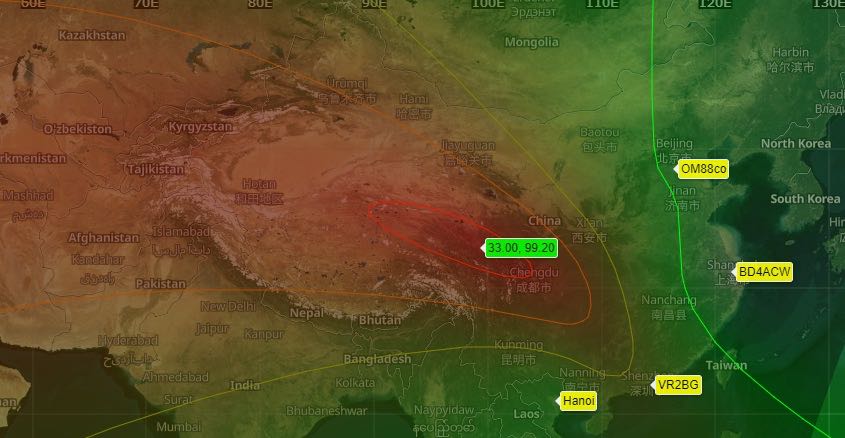
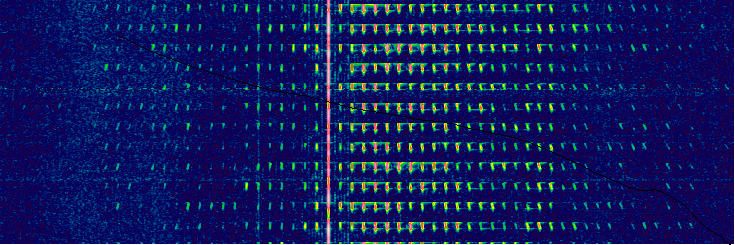
Numbers Station UVB-76: A New Buzzer Twin on 4810 kHz
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Tom (DF5JL), who writes:
Who doesn’t know the mysterious station “The Buzzer” on 4625 kHz – but now it gets even more exciting: Because since today “The Buzzer” has a twin that transmits on 4810 kHz – fully synchronous. And to make to put a scoop on it: location is apparently near Changdu in China.
Thanks for the tip, Tom!
Yes, I noticed that our friend, Tudor Vedeanu, recently posted a recording of the new Buzzer twin on 4810 kHz:
I’m curious if the new Buzzer frequency is being used 100% of the time? Can anyone confirm?
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
MDZhB featured in BBC Future’s “Best of 2017”
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Golan Klinger, who shares the following article which was elected “Best Of 2017″ on the BBC Future website:
“MDZhB” has been broadcasting since 1982. No one knows why.
In the middle of a Russian swampland, not far from the city of St Petersburg, is a rectangular iron gate. Beyond its rusted bars is a collection of radio towers, abandoned buildings and power lines bordered by a dry-stone wall. This sinister location is the focus of a mystery which stretches back to the height of the Cold War.
It is thought to be the headquarters of a radio station, “MDZhB”, that no-one has ever claimed to run. Twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, for the last three-and-a-half decades, it’s been broadcasting a dull, monotonous tone. Every few seconds it’s joined by a second sound, like some ghostly ship sounding its foghorn. Then the drone continues.
Once or twice a week, a man or woman will read out some words in Russian, such as “dinghy” or “farming specialist”. And that’s it. Anyone, anywhere in the world can listen in, simply by tuning a radio to the frequency 4625 kHz.
It’s so enigmatic, it’s as if it was designed with conspiracy theorists in mind. Today the station has an online following numbering in the tens of thousands, who know it affectionately as “the Buzzer”. It joins two similar mystery stations, “the Pip” and the “Squeaky Wheel”. As their fans readily admit themselves, they have absolutely no idea what they are listening to.[…]
Click here to continue reading the full article on the BBC Future website.