Here’s an opportunity for both ham radio operators and SWLs to log this special event air mobile station throughout June and July. Based on WB6RQN’s flight path, almost everyone should have an opportunity to put WB6RQN in the logs!
The following excerpt has been copied from the Project Amelia Earhart website:
About Ham Radio on the Spirit
Brian Lloyd has a powerful radio system aboard the Spirit. The radio communicates on High Frequency (HF) shortwave using Single Sideband (SSB), and anyone can tune in to these transmissions who has the proper type of radio receiver. Listen for WB6RQN, that’s Brian’s Ham radio callsign. Ham radio operators around the world are invited to communicate with Brian while he is on the air in international airspace using the Ham bands. HF radio is dependent on ionospheric conditions to be heard over long distances, and it may change rapidly with the space weather or other factors.
Ham Radio Technical Information
Ham Radio Callsign: WB6RQN
Operator Name: Brian
QSL Via: eqsl.cc Electronic QSL system
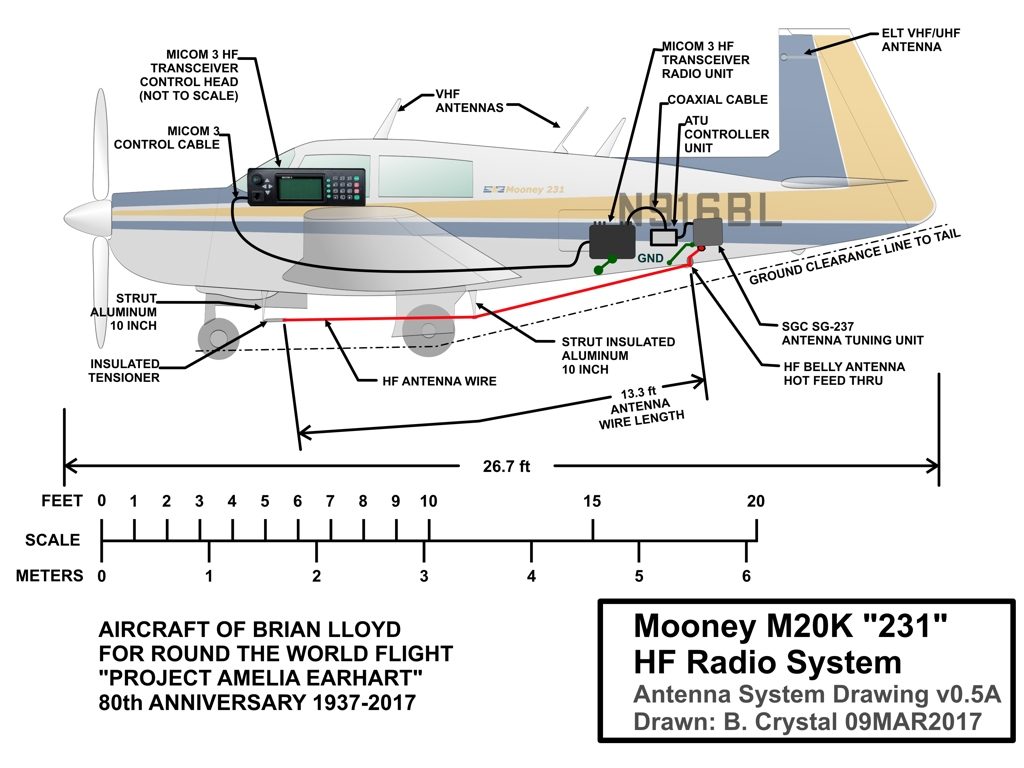
HF Radio: Mobat model Micom 3, commercial HF transceiver
HF Power: Maximum power 125 Watts, 2-30 MHz
HF Antenna: Tapered Towel Rack type Belly Wire, with Automatic Tuning Unit (ATU)
HF Modes of Operation: SSB Voice or ALE
Ham Callsign Phonetics: Whisky Bravo Six Romeo Quebec November , Listen:
Schedule of Possible Upcoming HF Radio Operation in 2017
31 May: Texas to Miami
01 June: Depart Miami. Embark on Round-the-World flight
02 June: Caribbean Sea area
03 June: South America area, Atlantic Ocean
05-06 June: South America, Atlantic Ocean, Brazilian Coast
07 June: Atlantic Ocean
08-09 June: Western Africa area
10 June: Eastern Africa area, Red Sea
11 June: Arabian Peninsula, Arabian Sea
12-15 June: South Asia, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean
16-18 June: SouthEast Asia, Adaman Sea, Indian Ocean
19-23 June: SouthEast Asia, Gulf of Thailand, Java Sea
24 June: Timor Sea area to Australia area
30 June – 4 July: Australia area, Tasman Sea, to New Zealand
14 July: New Zealand to Fiji, South Pacific Ocean
15 July: Fiji to Howland Island overflight, Pacific Ocean
16 July: Hawaii, Pacific Ocean
17-18 July: Hawaii to California, Pacific Ocean
19-21 July: California area
22-23 July: Western USA to Kansas area
24-28 July: Oshkosh Wisconsin USA for AirVenture
29 July: Oshkosh to Texas
Note: All dates and flight locations are approximate and tentative. Please see the Live Tracking Map for actual locations and flight movements.

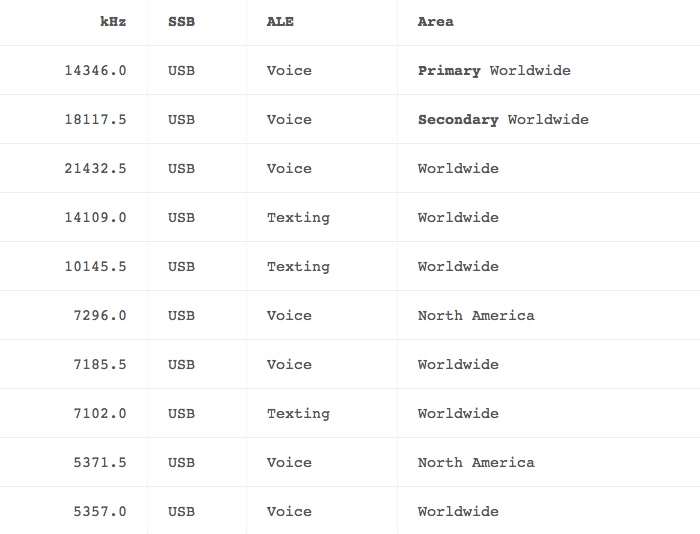
Ham Radio Frequencies of Operation for Spirit Flights
HF Frequencies for Ham Radio SSB Voice QSOs and DX:
- Ham QSO activity may occur at any time while the airplane is in International airspace, USA, or some other areas.
- Ham operation may happen while Brian is not busy with flight operations
- There may be unexpected interruptions during a QSO
- Please be especially courteous and patient, because his first priority is to pilot the plane.
Simplex or Split? Most of the time, WB6RQN will use simplex, listening and transmitting on the same HF frequency. But, sometimes Brian may ask calling stations to transmit “UP 5” split. When using UP 5 split, your transmit frequency must be exactly 5 kHz above WB6RQN. The plane’s HF radio is channelized, and it does not have an S-meter.
Click here for WB6RQN DX cluster spots.
Brian said, “During the actual flight I can talk on ham radio when I’m not using the HF radio to make position and status reports to Air Traffic Control. I will probably get 10 to 15 minute windows when I will be able to work ham stations on the HF bands occasionally. I have never been a contester, so my QSO rate will probably be lower than most ham operators would like.”
HF Channel Frequencies for Ham Radio ALE Activity:
- Activity using common Amateur Radio standard 2G-ALE Automatic Link Establishment may occur on the following scanned channels when Brian is not busy with flight operations.
- ALE activity may occur at any time while the airplane is in International airspace, USA, or some other areas.
- Whenever the ALE soundings of WB6RQN are heard, operators are invited to call on any one of these channels using an ALE Individual Call and link with WB6RQN.
- When linked on an ALE Voice channel, the preferred QSO method is Upper Sideband Voice.
- If a text is to be sent, use AMD and include the AMD text within the initial Individual Call.
- Do not expect a wordy text reply, because there is usually no QWERTY keyboard connected to the ALE radio in the cockpit.
- Anyone copying soundings, calling, or other types of reports is encouraged to post ALE reception logs on the HFLINK.NET website.
SWL and UTE Monitoring of HF Aero Frequencies
For SWLs (Shortwave Listeners) or UTEs (Utility Monitors), it is possible to listen to Spirit on the Air Traffic Control (ATC) HF Aeronautical frequencies with an SSB (Single Sideband) receiver. More information about listening to Spirit on HF Aero, click here.
Tour of the HF Radio System in Spirit
For more information, click here to view the Project Amelia Earhart website.