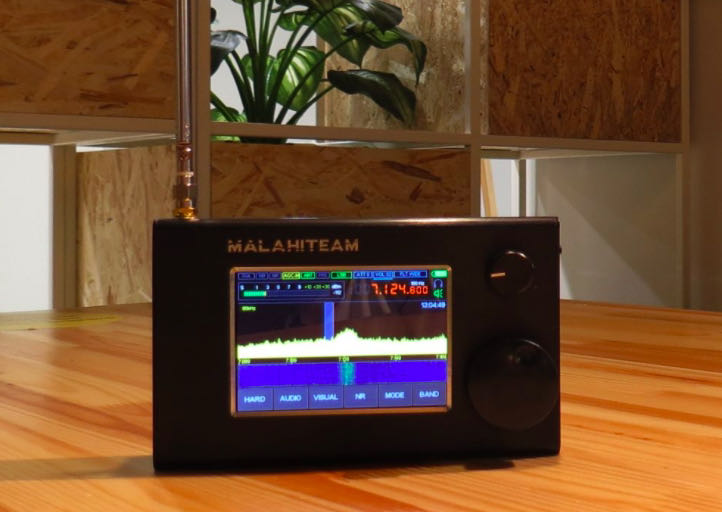
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Dan Robinson, for the following guest post and review:
 Two Chinese Clones: A Look at Noise Levels
Two Chinese Clones: A Look at Noise Levels
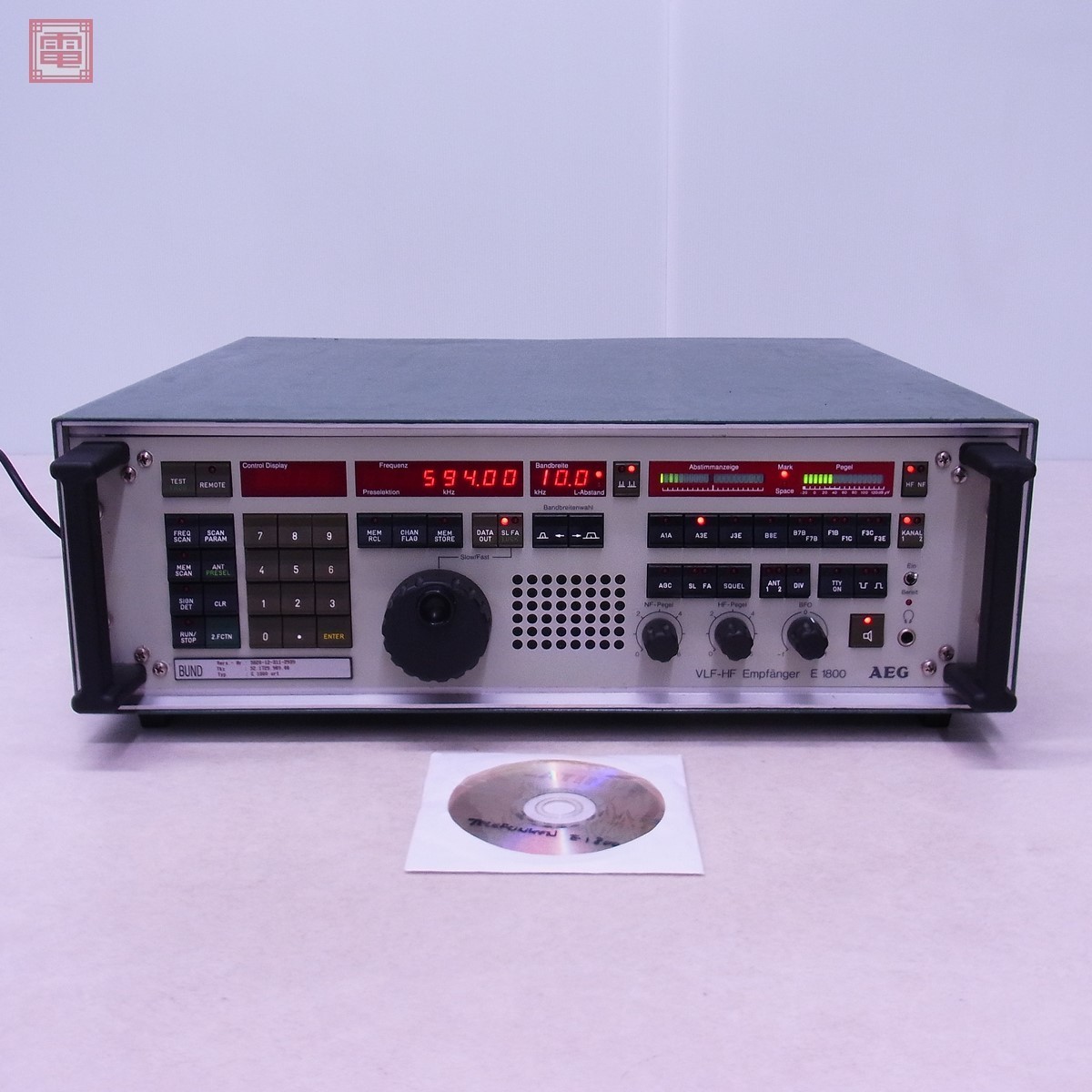
Arriving recently here in the radio shack, were a Chinese clone under the name of “Fire Brothers” and another under the name HFDY. I thought it would be constructive to note the key differences between these two clones, both of which are running Malahit 1.10c firmware, and post some video of a brief comparison.
A note in advance of any comments – I am primarily a HF listener so these comparisons do not cover frequencies above 30 MHz. For those whose focus is on higher frequencies I recommend looking through the many comments on the Malahit Facebook group and Telegram by those who use these receivers in those ranges.
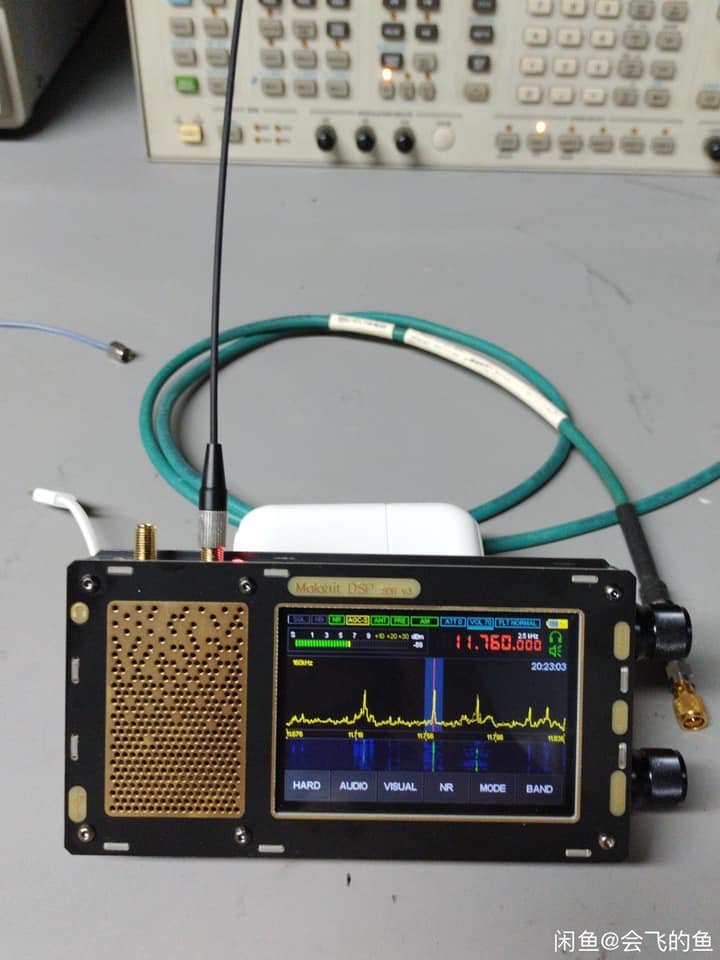
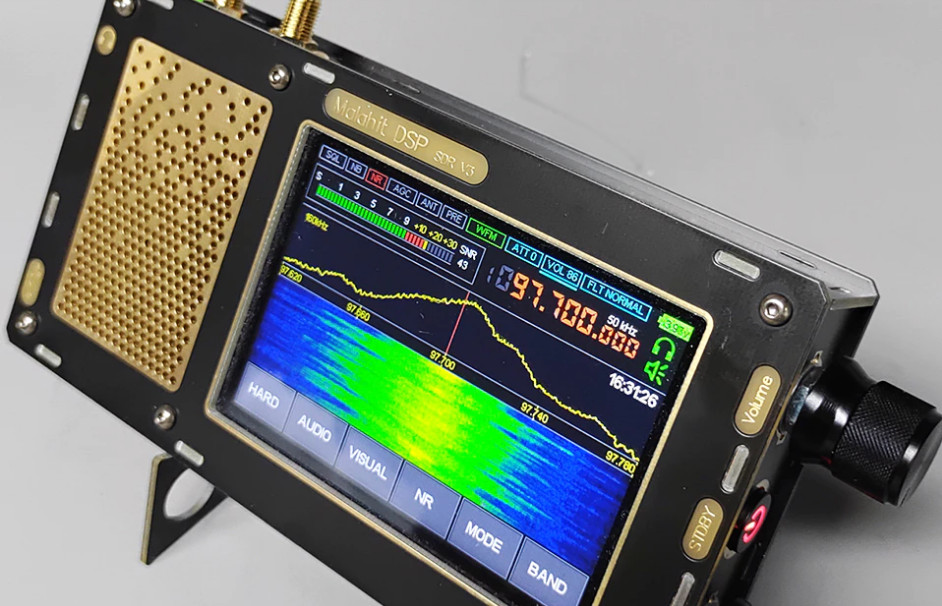
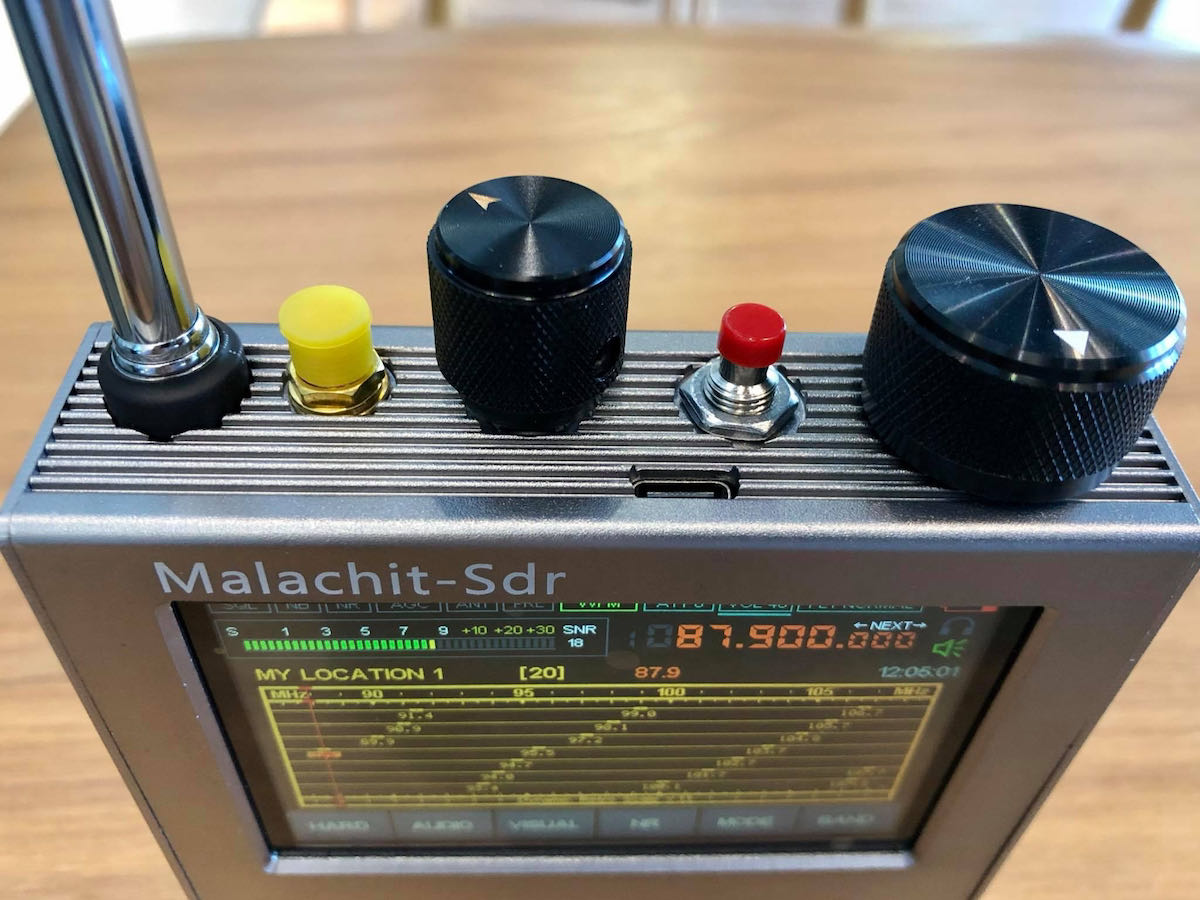
HFDY
- Constructed of metal-like material (a correction from my previous articles that this is fiberglass of the kind used in printed circuit boards – thanks to Georgiy of Malahiteam for pointing this out)
- Front speaker grille is gold color and appears to be metal but may be fiberglass as well – audio is quite good
- Two top-mounted antenna jacks, one 50 ohm, the other Hi-Z (makes switching between HF and FM/VHF reception easier) with in-use LED indicators
- Two high quality right side mounted black metal encoder knobs with large power button (clear printed Frequency/STDBY/Volume printed on panel)
- Cabinet held together with TORX screws
- 1.10c firmware
- Receiver is elongated left to right to accommodate left side front-firing speaker, but is thinner overall and could be easily placed in a pocket though not recommended to prevent damage
- Like every one of these SDRs, suffers from body sensitivity to touch which reduces signal levels unless some sort of additional ground is attached to cabinet
- Internal flat-type Lithium battery of 3300 mAh though apparently capable of fitting up to 8000 mAh