
I am asked this question, or a variation of it, almost every week:
“I’ve been thinking about buying a shortwave radio, but have heard that shortwave is dying out. Is there actually anything to listen to on shortwave? Should I even bother?”
It’s no wonder I get asked this question so much. First of all, the root website for the SWLing Post is SWLing.com, which is dedicated to teaching people the basics of using a shortwave radio. Indeed, if you search the internet for shortwave radio reviews or how to use a shortwave radio, you’ll most likely see this site somewhere near the top of the search results. So it makes sense that many of our readers are just starting out in shortwave.
But the primary reason people wonder about shortwave’s vitality and want to check its pulse, is due to recent news about shortwave broadcasters leaving the spectrum. Most recently, Radio Canada International, Radio Netherlands Worldwide, Radio Bulgaria have all closed up shop, and broadcasters like the BBC World Service and Vatican Radio have trimmed down their shortwave offerings. It’s unfortunate, and does make the continuation of shortwave seem doubtful to those who know less about it.

The Edward R. Murrow Tranmission Station’s slewable curtain antenna.
Question: So is there anything to listen to? Answer: Absolutely!
Regular shortwave radio listeners already know the answer to this question. Sure, the landscape of the shortwaves is changing, but it’s such a vast landscape that, even with a few major players dropping out, there is still so much to hear and appreciate. In fact, we’ve only been talking about governmental international broadcasters, in the main–which doesn’t even include pirate radio, clandestine stations, utility stations, religious networks, spy numbers stations, digital modes, and ham radio communications. Among others.
Doubt me? Well, then–check this out:
250 kHz of 31 Meters on a Friday afternoon

The WinRadio G31DDC “Excalibur”
Last Friday, I spent a pleasant afternoon reviewing the WinRadio Excalibur software defined receiver (SDR). Perhaps my favorite feature of many modern software defined receivers is their ability to record not only individual shortwave radio broadcasts, but also record radio spectrum. In other words, instead of recording a single station on 9,555 kHz, the WinRadio Excalibur (and similar SDRs) could easily record everything between, say, 9,410 and 9,635 kHz. Later, you can play back the spectrum to listen to and record individual broadcasts as if they were live. At least, this is exactly what I did last Friday at 20:00 UTC.
Fast forward to yesterday: While listening and tuning through the Friday spectrum, I once again realized how many stations are crammed into this relatively small chunk of the shortwave spectrum. Yet I only captured about 250 kHz, or .25 MHz of shortwave spectrum. To put this in perspective, this is a chunk of spectrum so small, you could fit four of them between 95 and 96 MHz on your car’s FM dial.
And what did I find? A lot of stations–and a lot of variety! In fact, I then went through and recorded 8 samples of the stronger broadcasts.
Here is some of what I heard just in that wee swatch of spectrum:
 Voice of Greece – 9,240 kHz
Voice of Greece – 9,240 kHz
 Voice of Iran – 9,460 kHz
Voice of Iran – 9,460 kHz
 WTWW – 9,478 kHz
WTWW – 9,478 kHz
 Deutsche Welle – 9,490 kHz
Deutsche Welle – 9,490 kHz
 Radio Riyadh – 9,555 kHz
Radio Riyadh – 9,555 kHz
 Radio Marti – 9,565 kHz
Radio Marti – 9,565 kHz
 North Quebec Service – 9,625 kHz
North Quebec Service – 9,625 kHz
 Voice of Turkey – 9,635 kHz
Voice of Turkey – 9,635 kHz
Here is how the actual spectrum chunk appeared on the Excalibur’s display:
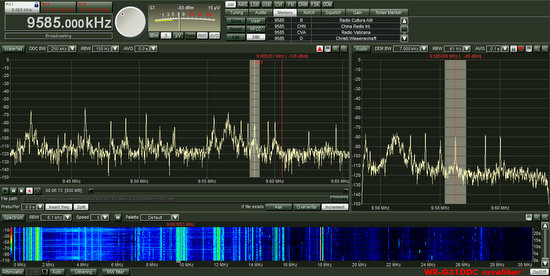
Note from the DDC spectrum window (the one immediately below the tuning knob and S Meter) that there are many, many other stations–indicated as spikes in the spectrum, above–that I did not bother to record.
I didn’t set out to find the most active piece of shortwave spectrum–I chose this one pretty much by chance.
Is shortwave radio dead? Only if you’re not listening
Perhaps the real fascination I find in listening to recorded spectrum, as I did above, is that each time I go back through a recording, listening carefully, I find so many other items that I would have otherwise missed. In other words, the better your ears, the more you will hear. And there’s lots to hear.

A good portable radio, like the C.Crane CCRadio-SW, can easily receive the major international broadcasters and even some low power regional shortwave stations.
So, what are you waiting for?
Prove it to yourself. Pull out your portable radio, your tabletop, your SDR or your general coverage ham radio transceiver, and just listen. There’s still a vast, informative, oftentimes mysterious world out there on the shortwaves, simply waiting for your ears.
Join me in the Shortwave Radio Archive Project: post coming soon!
 Yesterday, like most Saturday mornings, I sipped my coffee while listening to ABC’s Saturday Night Country from Radio Australia’s Shepparton shortwave transmission site on 9.58 MHz.
Yesterday, like most Saturday mornings, I sipped my coffee while listening to ABC’s Saturday Night Country from Radio Australia’s Shepparton shortwave transmission site on 9.58 MHz.

 Pirate radio is perhaps one of the most dynamic aspects of the diverse landscape of SWLing. In direct contrast with major broadcasters, many of whom are now thinning out their offerings, pirate radio just seems to adapt and grow.
Pirate radio is perhaps one of the most dynamic aspects of the diverse landscape of SWLing. In direct contrast with major broadcasters, many of whom are now thinning out their offerings, pirate radio just seems to adapt and grow.
 For your listening enjoyment: Voice of Greece (9,420 kHz), Radio Croatia (9,925 kHz) and Radio Romania International (9,700 kHz). The Voice of Greece and Radio Croatia broadcast an extensive mix of music; while Radio Romania International offers their English and French hours.
For your listening enjoyment: Voice of Greece (9,420 kHz), Radio Croatia (9,925 kHz) and Radio Romania International (9,700 kHz). The Voice of Greece and Radio Croatia broadcast an extensive mix of music; while Radio Romania International offers their English and French hours.



