 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Fastradioburst23, who shares the WSTL flyer above announcing a broadcast on Sunday, February 13, 2022 at 2300 UTC on 9395 kHz (WRMI).
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Fastradioburst23, who shares the WSTL flyer above announcing a broadcast on Sunday, February 13, 2022 at 2300 UTC on 9395 kHz (WRMI).
Looks like the kettle’s on at WRMI! Thank you for the tip!
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Sam Alcorn, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Sam Alcorn, who writes:
A query:
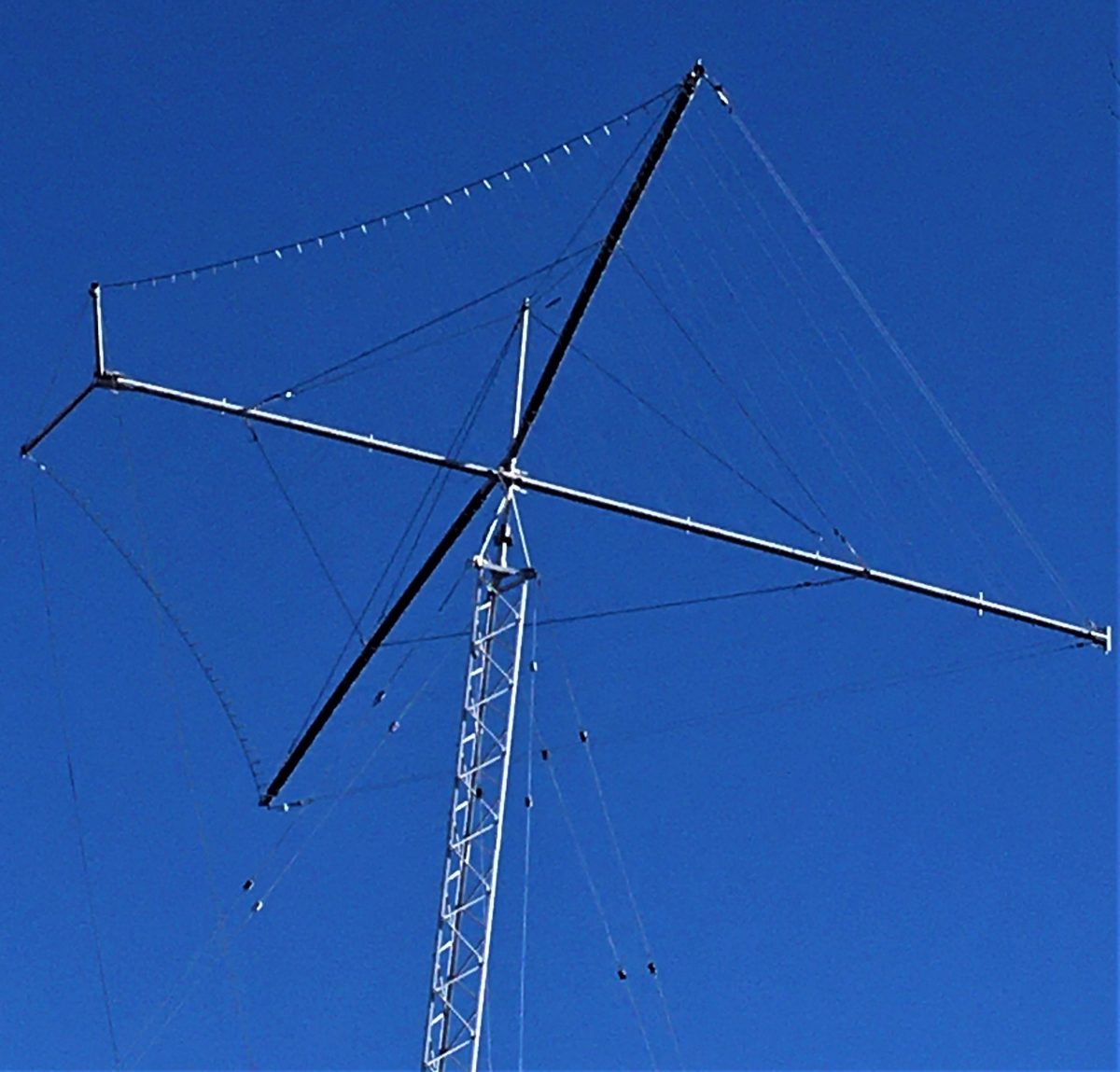
Many of the embassies in Washington, D.C., have impressive-looking antenna systems. Pictured (above) is the array atop the Romanian Embassy on 23rd St. NW. It looks well maintained and I’ve been wondering if they, and others, are operational – especially in this Internet era. Can anyone here shed any light on these operations? Are they still used? Frequencies? Power?
Sam Alcorn
Washington, D.C. 20009
Thank you for your inquiry Sam. I, too, have noticed impressive antenna arrays on some of the DC embassies. Perhaps someone in the SWLing Post community can shed a little light? Please comment!
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Much thanks to the many contributors who shared the following items:
Drivers of certain vehicles in Seattle and other parts of Western Washington are shouting at their car radios this week. Not because of any particular song or news item that’s being broadcast, but because an apparent technical glitch has caused the radios to be stuck on public radio station KUOW.
The impacted drivers appear to all be owners of Mazda vehicles from between 2014 and 2017. In some cases the in-car infotainment systems have stopped working altogether, derailing the ability to listen to the radio at all or use Bluetooth phone connections, GPS, the rear camera and more.
According to Mazda drivers who spoke with GeekWire, and others in a Reddit thread discussing the dilemma, everyone who has had an issue was listening to KUOW 94.9 in recent weeks when the car systems went haywire.
KUOW sounded unsure of a possible cause; at least one dealership service department blamed 5G; and Mazda told GeekWire in an official. [Continue reading…]
While it’s been widely contested who actually invented the first radio (both Italian physicist Gugliemo Marconi and Serbian-American inventor and engineer Nikola Tesla were fighting for the first patent, per PBS), it was Marconi who came out top in 1904, when the U.S. Patent Office officially dubbed him the inventor of the new breakthrough technology. According to APM Reports, in 1920, Americans had their first commercially licensed radio station in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: KDKA. That number quickly rose after KDKA broadcast the election that saw Warren G. Harding become the 29th president, and by 1924, 500 stations were available for listening.
By 1930, over “40% of American households owned a radio,” per APM Reports. This became known as “The Golden Age of Radio.” As revealed by PBS, in 1930, 12 million Americans owned radios — growing to a whopping 28 million by the end of the decade.
Access to the radio came at a turbulent time in history. As the Great Depression caused widespread suffering for millions of Americans (via History), the households that could afford a radio saw it as a welcome source of entertainment and news that made them feel connected to the rest of the country. These days, with over 15,445 radio stations available in the U.S., it’s clear the radio still remains relevant, but its impact on society truly began nine decades ago. Let’s take a look at the real reason the 1930s were considered “The Golden Age of Radio.” [Continue reading…]
ST. PETERSBURG, February 7. /TASS/. The International Consortium for the Preservation of Arctic Cultural Heritage, based at the Russian State Hydrometeorology University (RSHU), initiated a cross-border radio broadcast in languages of the North’s indigenous peoples, the university’s representative in Moscow Andrei Bryksenkov told TASS.
An application for the broadcast has been filed with the Arctic Council. “The application must be filed from two countries, and we plan to go along with Norway – with the Sami Radio, which is a part of Norway’s big television and radio concern. <…> The idea has been supported at all levels. As for the cross-border broadcast, we, probably, will begin from the shortwave broadcast, as it covers bigger territories and is less costly,” he said.
At the initial stage, the pilot broadcast will be organized on the territories of Finland, Norway and Russia. The project’s initiators are ready to cooperate with other countries. “One transmitter in Krasnoyarsk may cover 80% of the Russian North. Norway has such a transmitter, which covers the Scandinavian territory. Another two transmitters are on Alaska,” he continued. Later on, the broadcast will be also on middle and long waves, thus one frequency will carry 3-4 channels, he added. One of them will be in Russian and English, and the rest – in languages of the indigenous peoples.
The audience will learn about traditions, skills of the peoples living in the North. The content will fully focus on culture. The countries, participating in the project, will open newsrooms. “We hope the general center, which will coordinate the project, will be at the Arctic Council,” he said.
The International Consortium for the Preservation of Arctic Cultural Heritage includes St. Petersburg’s committee on the Arctic, the Arctic museum and exhibition center in St. Petersburg, the Association of indigenous low-numbered peoples of the North, Siberia and Far East, and others. [Read full article…]
The modernization of radio’s regulatory rulebook that began under the prior administration continues at the Federal Communications Commission. It is slated to approve a half dozen changes at the Commission’s February meeting, in what Chair Jessica Rosenworcel says is a “cleaning up” of the broadcast radio rules.
“The Commission’s current rules for full-power and translator radio stations contain a number of provisions that are redundant, outdated, or in conflict with other rules,” said Rosenworcel. She said the proposal would “update and clean up” those provisions “in order to reduce any potential confusion, alleviate unnecessary burdens, and make sure our rules reflect the latest technical requirements.”
The proposed order (MB Docket No. 21-263) would update six rules, while scrap plans to change another. They include –
Eliminate Transmitter Power Limit Rule For AMs.
The draft order says the FCC has tentatively concluded the rule is “outdated and unnecessary” given its current reliance on actual operating antenna input power as the most accurate and effective means of ensuring that AM stations adhere to their authorized power limits. The FCC also agreed with comments filed by the National Association of Broadcasters that said the elimination of the technical restriction will allow AMs of any class to use transmitters of any rated power. That, it says, will benefit all AMs by broadening the market of transmitters, enhancing the secondary market for AM transmitters, and reducing the number of transmitters that need to be disposed of.
Clarify AM Fill-in Area Definition
The FCC is poised to amend the definition of an “AM fill-in area” used when an FM translator simulcasts an AM station. [Continue reading…]
On Thursday, February 3 at 1:13 p.m. EST, Falcon 9 launched 49 Starlink satellites to low Earth orbit from Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Falcon 9’s second stage deployed the satellites into their intended orbit, with a perigee of approximately 210 kilometers above Earth, and each satellite achieved controlled flight.
SpaceX deploys its satellites into these lower orbits so that in the very rare case any satellite does not pass initial system checkouts it will quickly be deorbited by atmospheric drag. While the low deployment altitude requires more capable satellites at a considerable cost to us, it’s the right thing to do to maintain a sustainable space environment.
Unfortunately, the satellites deployed on Thursday were significantly impacted by a geomagnetic storm on Friday. These storms cause the atmosphere to warm and atmospheric density at our low deployment altitudes to increase. In fact, onboard GPS suggests the escalation speed and severity of the storm caused atmospheric drag to increase up to 50 percent higher than during previous launches. The Starlink team commanded the satellites into a safe-mode where they would fly edge-on (like a sheet of paper) to minimize drag—to effectively “take cover from the storm”—and continued to work closely with the Space Force’s 18th Space Control Squadron and LeoLabs to provide updates on the satellites based on ground radars.
Preliminary analysis show the increased drag at the low altitudes prevented the satellites from leaving safe-mode to begin orbit raising maneuvers, and up to 40 of the satellites will reenter or already have reentered the Earth’s atmosphere. The deorbiting satellites pose zero collision risk with other satellites and by design demise upon atmospheric reentry—meaning no orbital debris is created and no satellite parts hit the ground. This unique situation demonstrates the great lengths the Starlink team has gone to ensure the system is on the leading edge of on-orbit debris mitigation. [Read at SpaceX…]
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!


From the Isle of Music, February 13-19, 2022:
This week we honor World Radio Day and St. Valentine’s Day with music from the 1999 Bridge To Havana concert featuring prominent musicians from the US and Cuba.
The broadcasts take place:
1. For Eastern Europe but audible well beyond the target area in most of the Eastern Hemisphere (including parts of East Asia and Oceania) with 100Kw, Sunday 1500-1600 UTC on SpaceLine, 9400 KHz, from Sofia, Bulgaria (1800-1900 MSK)
2. For the Americas and parts of Europe, Tuesday 0100-0200 UTC on WBCQ, 7490 kHz from Monticello, ME, USA (Monday 8-9PM EST in the US).
3 & 4. For Europe and sometimes beyond, Tuesday 1900-2000 UTC and Saturday 1300-1400 UTC (NEW FOR B21) on Channel 292, 6070 kHz from Rohrbach, Germany.
If you don’t have a shortwave radio or are out of range, you can listen live to uplinks from various websdrs in Europe.
Our Facebook page is https://www.facebook.com/fromtheisleofmusic/
Our V-Kontakte page is https://vk.com/fromtheisleofmusic
Our Patreon page is https://www.patreon.com/tilford
Uncle Bill’s Melting Pot, February 13-19, 2022:
Episode 255 presents music from Botswana.
The transmissions take place:
1.Sunday 2300-0000 (6:00PM -7:00PM EST) on WBCQ The Planet 7490 kHz from the US to the Americas and parts of Europe
2. Tuesday 2000-2100 UTC on Channel 292, 6070 kHz from Rohrbach, Germany for Europe.
3. Saturday 0800-0900 UTC on Channel 292, 9670 kHz from Rohrbach, Germany for Europe with a directional booster aimed eastward.
Our Facebook page is https://www.facebook.com/UncleBillsMeltingPot/
Our V-Kontakte page is https://vk.com/fromtheisleofmusic
Our Patreon page is https://www.patreon.com/tilford
WBCQ 4790 kHz Test Update February 13-19 US dates (14-20 world dates), 2022
Propagation testing continues on 4790 kHz using 0100-0300 UTC every night. So far, the
signal has been good to excellent in most of eastern and central North America, problematic due to CODAR west of the Rockies and fair to good in much of continental Europe, especially Germany, the Czech Republic and Finland.
On February 14 world date 0100-0200 UTC, there will be a special tribute to World Radio Day and St. Valentine’s Day
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bob Colegrove, who shares the following guest post:
As recalled by Bob Colegrove
In his comment on my recent posting, Tinkering with History, Mario noted the dial on the featured radio, the General Electric P755A, sported two small triangles, one between 6 and 7, and the other between 11 and 14. He noted that these were civil defense markers intended to show the frequencies of 640 kHz and 1240 kHz, respectively, and that these were characteristic of AM radios produce in the US roughly between 1953 and 1963. Since two full generations have been born and raised to adulthood since that time, and I can’t find any related posting here, I thought it might be useful to bring this subject to light.
In spite of otherwise economic prosperity and general wellbeing, these years were nevertheless filled with anxiety about the prospects of all-out war. Children of the time (myself included) were being shown how to hide under their school desks, and some of their parents were going so far as to construct air-raid shelters in their basements, and stock them with enough provisions to supposedly outlast any catastrophe. So it was that CONELRAD came into being in 1951. The idea was, that in case of a National emergency, all radio and TV stations would go off the air, and only certain medium wave radio stations would stay on either 640 kHz or 1240 kHz. They would remain on for a few minutes and then other stations would take over in a round robin arrangement – this to deter homing by hostile bombers. Needless to say, quickly changing over transmitters and antennas to one of these two frequencies did not bode well for the equipment and there were many failures in subsequent tests. Note that, as originally conceived, the system did not provide for local weather emergencies or other situations.
The banner photo at the top of this posting shows a portion of the Hallicrafters S-38E receiver which conformed to Government law of the time required for marking all AM dials. An S-38E just like it was my first genuine multi-band radio in 1959. Assuming good alignment, the dots next to the CD triangles indicated the 640 kHz and 1240 kHz frequencies. When a test came on, you didn’t have to fish for it, since CONELRAD was the only service transmitting.
Going back to the radios described in Tinkering with History, GE took this one step further. The figure below shows a portion of the dial on a GE P806A. Note the nub on the outer edge of the dial under the triangle at 1240 kHz. There is another nub on the edge at 640 kHz. Together with the raised triangular dial pointer molded on the cabinet, they provided a braille system, so that someone visually impaired could easily tune to a CONELRAD frequency.
As technology improved, CONELRAD transitioned to the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) in 1963, and subsequently the Emergency Alert System in 1997. A more thorough description of CONELRAD can be found on Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CONELRAD. Reprint of an April 1955 Radio & Television News article describing the construction of a transistor CONELRAD receiver is at https://www.rfcafe.com/references/radio-news/conelrad-radio-television-news-april-1955.htm.
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Germany and the EU have condemned Russia’s decision to shut down the Moscow bureau of international public broadcaster Deutsche Welle (DW).
All DW’s staff have lost their press accreditations and the channel is barred from broadcasting in Russia.
Germany’s culture minister said the move was “not acceptable in any way”.
Russia argued it was retaliating after German regulators decided a new Russian state-run TV channel, RT DE, did not have a suitable licence to operate.
Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova appeared to offer an olive branch to the German government on Friday, saying that if Germany moved to “normalise the situation”, then Russia would too.
RT has channels in English, French and Spanish and launched its German-language satellite channel in December 2021, using a licence from Serbia, outside the European Union. [Continue reading…]
The City of Schenectady, home of General Electric, was once a nursery for broadcasting. One of the nation’s first commercial radio stations began broadcasting 100 years ago. A new exhibit at the Museum of Innovation and Science is celebrating the history of WGY.
WGY was created by GE in 1922 and still operates today under different ownership as a news/talk station. The station’s history is currently on display at miSci in a photo exhibit called WGY: Radio’s Laboratory Celebrates Its Centennial.
Chris Hunter, the museum’s Vice President of Collections and Exhibitions, took me on a tour of the exhibit located in a new gallery inside the museum.
“So, it was about 10th commercial station licensed in 1922. And because it was formed by GE’s publicity department, and not so much the engineers that formed a lot of the other early radio stations, they really placed a premium on entertainment and, kind of, the development of broadcasting.” [Continue reading…]
After a successful AWA on-air sending of the historic 1921 Trans-Atlantic message in December of last year, using the AWA replica of the 1921 transmitter, plans are now in place to do it again only this time to offer two-way QSO’s with all stations wishing to participate.
The QSO party begins on Saturday evening, February 26, at 6:00 p.m. EST, or 23:00 GMT. AWA operators at the museum site in Bloomfield, NY will begin calling CQ on 1.821 MHz, CW, and will listen on or about that frequency for callers. We will work as many folks as we hear in order received and continue to do so until all amateur stations on the planet are in the log or propagation goes away, which ever happens first!
No QSL’s are required for you to receive a nice full sized color certificate confirming your QSO with W2AN/1BCG. Simply send your QSO information via email to [email protected] and the personalized certificate will be sent to the sending email address.
n a gray Friday afternoon last spring, Steve Galchutt sat high atop Chief Mountain, an 11,700-foot peak along Colorado’s Front Range. An epic panorama of pristine alpine landscape stretched in almost every direction, with Pikes Peak standing off to the south and Mount Evan towering just to the west.
It was an arresting view, and the perfect backdrop for a summit selfie. But instead of reaching for his smartphone, Galchutt was absorbed by another device: a portable transceiver. Sitting on a small patch of rock and snow, his head bent down and cocked to one side, he listened as it sent out a steady stream of staticky beeps: dah-dah-di-dah dah di-di-di-dit. “This is Scotty in Philadelphia,” Galchutt said, translating the Morse code. Then, tapping at two silver paddles attached to the side of the radio, he sent his own message, first with some details about his location, then his call sign, WG0AT.
At this point, a prying hiker could have been forgiven for wondering what, exactly, Galchutt was doing. But his answer—an enthusiastic “amateur radio, of course!”—would likely only have further compounded their confusion. After all, the popular image of an amateur-radio enthusiast is an aging, armchair-bound recluse, not some crampon-clad adventurer. And their natural habitat is usually a basement, or “ham shack,” not a windswept peak in the middle of the Rockies. [Continue reading…]
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
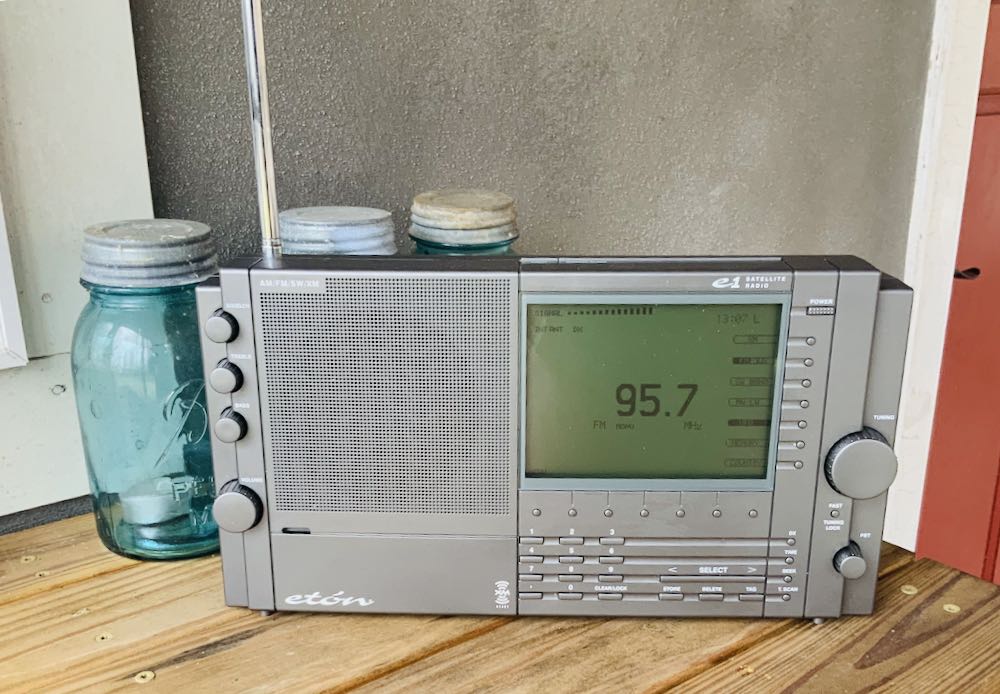 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Pavel Kraus, who shares the following guest post:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Pavel Kraus, who shares the following guest post:
I recently became the owner of an Eton E1 receiver, which I obtained on eBay from the USA.
The receiver is great, everything worked, error-free display. The only problem was that even FM and strong local stations did not play stereo even though stereo reception was set in the menu. The stereo text on the display flashed several times when the stations were not tuned in precisely, but after the stereo tuned, the text went out. I know that stereo reception is not the most important thing for this receiver, but it bothered me that there was a defect at all.
The Sanyo 3335 stereo decoder is used in this radio. The stereo reception switching threshold can be set with a 10kohm potentiometer which is connected to terminal 4 of the integrated circuit:
I disassembled the radio by loosening the screws on the back of the radio. The receiver is divided into two parts. I removed the XM module and disconnected the part of the radio with the display from the flat wires on the second printed circuit board of the radio.
I then removed the screws on the circuit board located at the back of the radio.
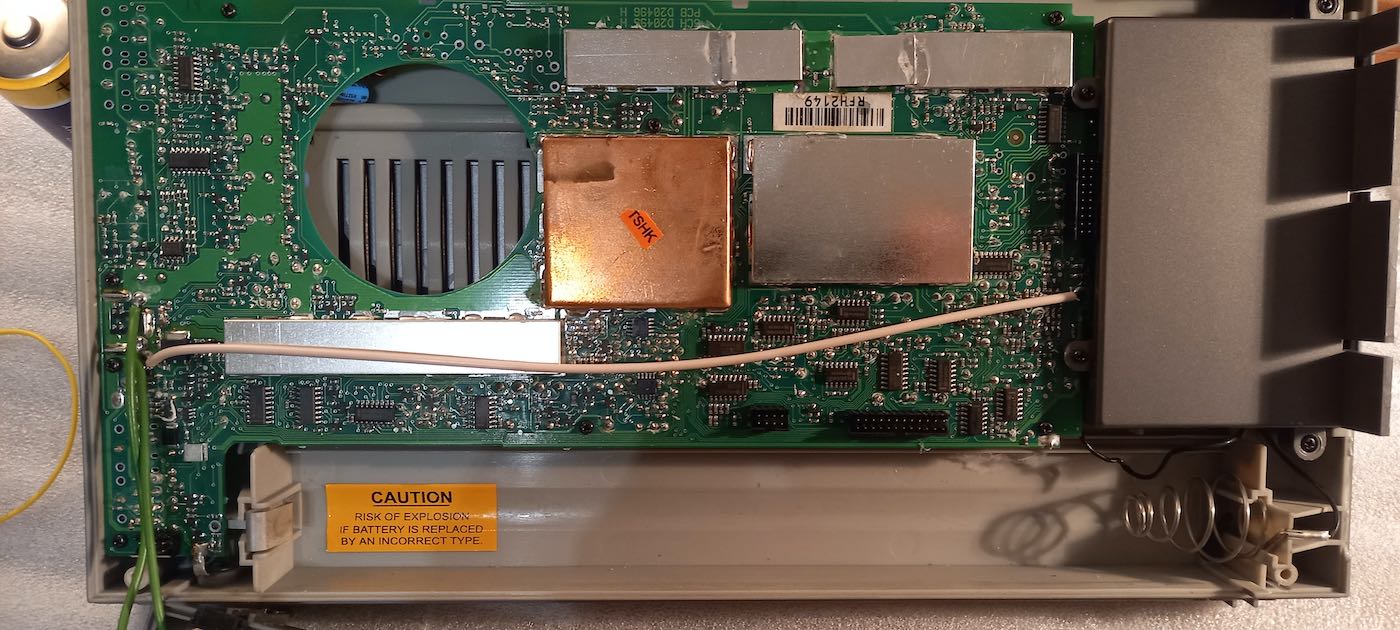 I removed the printed circuit board and found a matching resistor trimmer on the other side of the circuit.
I removed the printed circuit board and found a matching resistor trimmer on the other side of the circuit.
Then I connected these two points with a wire (when running on batteries) so that I could turn on the receiver:
After tuning in to a strong local transmitter, I carefully turned the trimmer until the stereo sign lit up and listening to the headphones made sure the sound matched the stereo. I repeated this at several local stations.
The receiver now plays stereo perfectly and the settings do not affect other parameters of the receiver. After assembling the radio, I was able to enjoy quality stereo reception.