Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Patrick Canler who writes to us from France and shares the following guest post which he translated into English:
The number of receivers on the market is quite large, and all are sold to be the “best”. I have thought it useful to compare materials using them in the shack as a neophyte SWL; going beyond the features in the brochures to talk about everyday utility. This article does not pretend to do “scientific” testing of the four receivers–skills and special equipment are needed and some specialized laboratories already do it.
The four receivers cover thirty years of electronics manufacturing; four different brands with their own technology and specifications. Over such period, technologies and innovations have evolved. One of the questions I had was: “Does efficiency give any receiver an advantage?”.
The Contenders:
NRD-535 from Japan Radio Company.
A reference of the 90s! It received 5 stars from WRTH (which publishes annually the almanac “World Radio and TV Handook”). The NRD-535 has conventional construction with an electronic card per function and discrete and analog filters.
This is a home station receiver, weighing in at 10 kg. The NRD-535 ceased to be produced in 1996, and its value second hand is growing due to its reputation.
AR7030 from AOR
Designed by the engineer who developed the LOWE receiver line, the AR7030 is also famous for its reception. It uses special ergonomics and a hybrid of software menus and conventional controls. Quite small, it is easily transportable, due its design that already uses SMC but keeps the analog filters.
IC-R75 ICOM
Modern device, classical format and renowned–the R75 is the only receiver tested that is still in production [Note: it was recently removed from production]. It uses CMS, combines analog and DSP filtering (the DSP option is present on the device under test). Its ergonomic design is intuitive and so too are controls and menus.
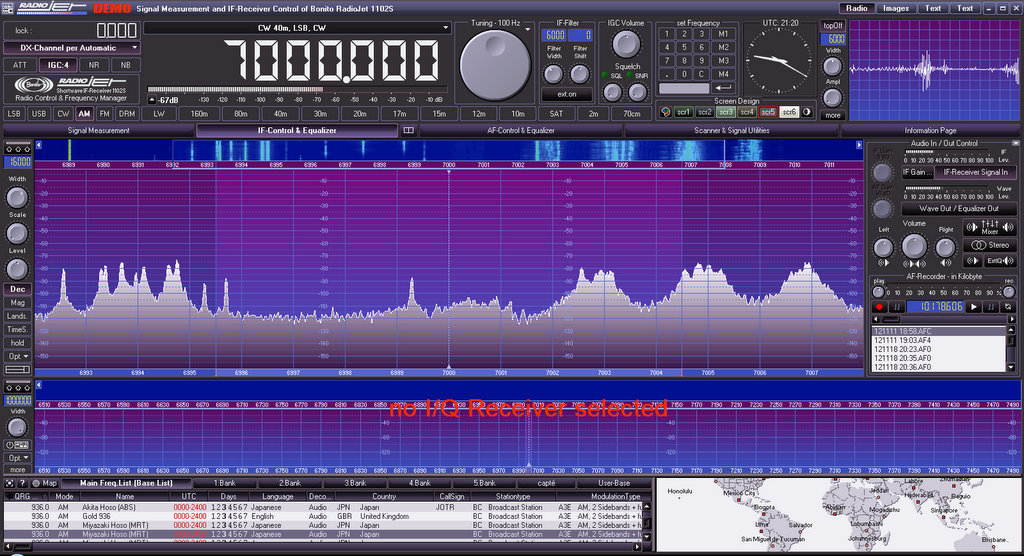
1102S RADIOJET Bonito,
The 1102S RADIOJET is the only unit in this comparison that is produced in Europe!
The Radiojet includes the latest developments in technology, its performance is simply stunning on the data/spec sheet. The application includes many tools (spectrograph, digital filters, IF and AF recorders, decoder, list of broadcast stations, etc.). It brings together all the SMC receiving electronics in a small box that can fit in a pocket.
The commands and tools are assigned to a software (highly evolved) that runs on the PC which is connected the SDR. The power of the PC also brings graphics, memory, recordings etc.
Why these four rigs?
In the beginning, and it was it which led me to be SWL, I acquired the RADIOJET based on its announced characteristics: sensitivity of “secret services”, adaptable to all cases with filters, graphics tools–“Star Wars equipment” is not it! Later I learned about 50 MHz and at the same time I was struggling to exploit the Radiojet SDR.
A good opportunity to purchase an ICOM R75 brought me back to conventional radio ergonomics. As time passed, I felt my listening skills improved with these 2 receivers and the receiver syndrome grew! A Kenwood R5000 joined the others for its VHF potential and HF reputation.
Then I discovered an NRD-525 on Ebay at a fair price point (rare)–it joined the group of receivers. The latter two were sold and replaced respectively by an AOR 7030 and by NRD-535. I really enjoyed the 525, but the 535 is even better.
In use, the RADIOJET and R75 have always posed problems with settings and sound quality. Kenwood reassured me about the fact that we could get some nice reception without fighting against the controls. validated by the AOR, the NRD 525 & 535. Perhaps I did not understand the manipulation of digital filters???
Now to the shack!
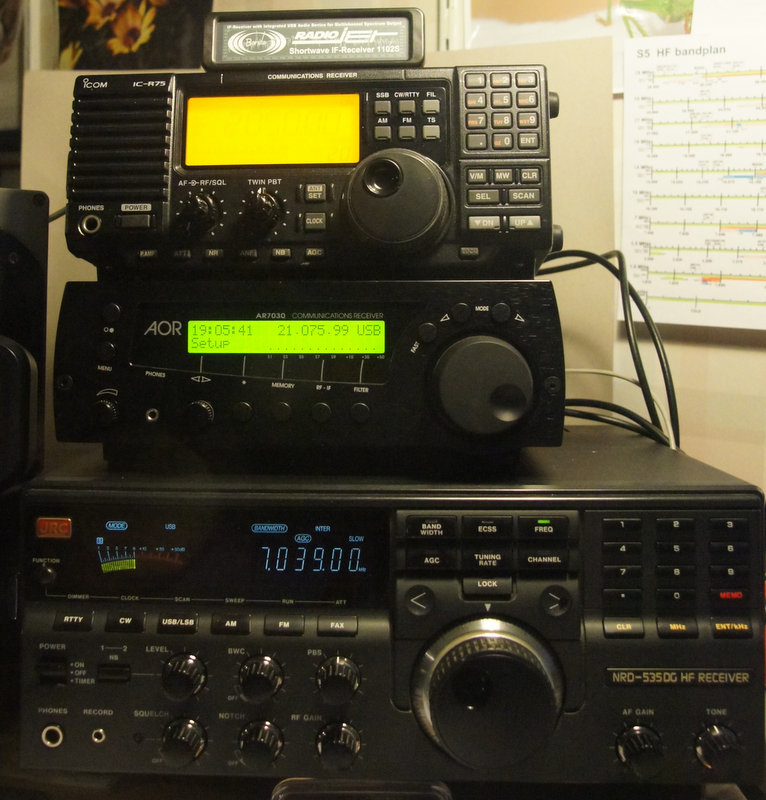
The four receivers are placed side by side, but arranged so as not to disturb each other (eg. the display of the ND535 disrupted the RADIOJET).
The antenna is a 25m random wire oriented East/West with 9:1 balun and its own ground. The passage from a receiver to the other is done by a conventional antenna switch.
All the tests were performed in one evening for constant conditions, there was a fairly present QRM which, was not too bad for comparison purposes. The tests were made in SSB or AM. Preliminary tests had shown that the results in digital modes (PSK31, JT65, ..) relied more on the decoder performance of the PC rather than the receiver. The tests increased from the lowest frequency detected this evening (Europe 1-163 kHZ) to the highest (Foreign Broadcast =15,545 MHz).
The highest frequencies, up to 30 MHz, were deserted in phone, at least for my installation.
The procedure was:
- Signal is detected from the spectrograph SDR: it typically “sees” almost inaudible signals.
- The candidate frequency is tuned on all four receivers
- I listening to all of the signals on all receivers, seeking to get the maximum performance, using all possibilities (notch, passband, IF Shift, integrated amplifiers, attenuator, etc.)
- Results are reported in the table below.
One can notice rather quickly:
- that age is not a handicap
- the number of functions is not always an advantage
- 1102S RADIOJET
Performance and capabilities above the rest (on paper) and requires being connected to a PC. At the present time, on an old Celeron 2Gb ram, the RadioJet’s application never saturated the CPU. The band spectrum display allows one to find the QSO, to filter theoretically perfectly, but it does not always equate to the understandability of the signal or give a pleasant audio. And the number of software features and functions complicates the signal manipulation. The sound is still a little metallic, perhaps due to the signal processing software. Its small size makes it a unbeatable mobile receiver for travel, functions are incredibly useful for those who master the RadioJet application. - AOR AR7030
Inherently simpler at face value–the AR7030 is ultra easy to use. It makes it easy for the user to find and tweak a candidate signal. It’s intuitive and has essential functions only. It has well-designed electronics. The AR7030 is also best receiver tested for handling strong signals without overloading (broadcasts stations or nearby hyper-kilowatted amateur radio operators) which seems to prove that it is designed for these stations. Its limit is the lack of adaptive notch filter types to clean the noise, which is still quite present when the QRM is there. (The newer version 7030+ has added features to help). Finally, it is the smallest stand-alone, portable and with 3 options of antennas connections. - ICOM R75
The R75 climbs up the frequency band all the way to 50 MHz, the only receiver tested with this frequency range. It enjoys an excellent reputation, and can be equipped with a DSP (digital signal processing) on audio. The DSP provides adaptive noise reduction and automatic notch, but has a relative effectiveness which is not always successful in clarifying the signal. Sometimes it adds an unpleasant “rattling”. In use, the interface is pretty intuitive–mixing commands by buttons and menus. Twin pass band tuning (PBT) is effective and allows for IF Shift and/or notch. The speaker is (very) small and gives an aggressive/harsh sound. This receiver is relatively small in size and lightweight. It has a mobile stand and is designed for a 12-14V power supply. - JRC NRD-535
The NRD-535 is the oldest tested–indeed, it was already discontinued before the other receivers were in production. A solid and reliable construction, good ergonomic with conventional front panel controls, good sensitivity, and a decent sized speaker have earned it status as a benchmark in its time. Very sensitive, it extracts the signals and, once found the right filter, gives it pleasant audio. Some signals are not completely cleaned but it does rarely less than others. The NRD-535 is designed for home use: it is heavy, almost 10 kg, and is contains several circuit boards which should not be too exposed to excessive shocks, especially considering they’re over 20 years old.
Summary
My ranking is as follows:
- JRC NRD-535 for its ease of use and ability to dig out a usable signal from the QRM.
- AOR AR7030 for its simplicity, portability and the fact that it extract good sound/audio quickly, even if a little noisy at times.
- Bonito RADIOJET for its small size and its extensive feature set. It is ultra-mobile with a laptop.
- ICOM R75 does the job and covers a wide frequency range. But lags in performance relative to the other receiver tested, with a “nasal” sound and a DSP that does not keep its intended promises.
About digital filters: the SDR and ICOM have them, the possibilities are extensive and allow adaptive filtering that others do not with analog filters. By cons they give a dry sound and sometimes add “snap” under whistles. Listening is overall less pleasant in comparison.
Receivers Advantages + / Disadvantages –
Bonito RADIOJET
+ Top technology, visual and many new features over the others on this point
– Complicated, metallic sound, emphasizing the sometimes painful receiver interaction with a computer mouse
Icom R75
+ Great value at the present time
– Audio and imperfect signal cleaning
AOR AR7030
+ Simple and effective
– Ideal companion if it had a notch filter: noise is present
JRC NRD-535
+ Effective sensitivity and clean audio
– Older technology, less portable
Note that this is a personal opinion: a computer geek will certainly get the most of performance and possibilities from an SDR like the Bonito RadioJet.
The NRD-535 shows its age, will one day reach the end of its useful life despite its robust construction. ICOM can cover up to 6m remaining mobile and has a good filter possibilities (DSP). The AOR is easy, fast and gives a correct listening, general purpose. It is the only one to pass the VLF.
The ideal then?
* RADIOJET for sensitivity,
* The RADIOJET for tools/features and functions
* AR7030 for the lower bands
* Icom for the higher bands
* NRD-535 for ergonomics
* AOR for portability
Personally, I use the NRD-535 for DXing (due to superior audio), the AR7030 for digital modes,
the RADIOJET to visually search for signals, and to sometimes clarify the signal even better and because it’s ultra-mobile and always in my PC case.
73,
Patrick F61112
Thank you, Patrick!
I should mention that I think you did a fine job translating your article into English for us! I would not be as successful writing an article in French!
I’ve never owned a JRC of any sort. If I ever found an NRD-535 for a good price, I would purchase one without hesitation. I’ve never spent much time on the AR7030 either. It’s simple “Lowe-like” front panel is quite appealing for field use. I found that the RadioJet audio is quite nice when paired with a good set of headphones.