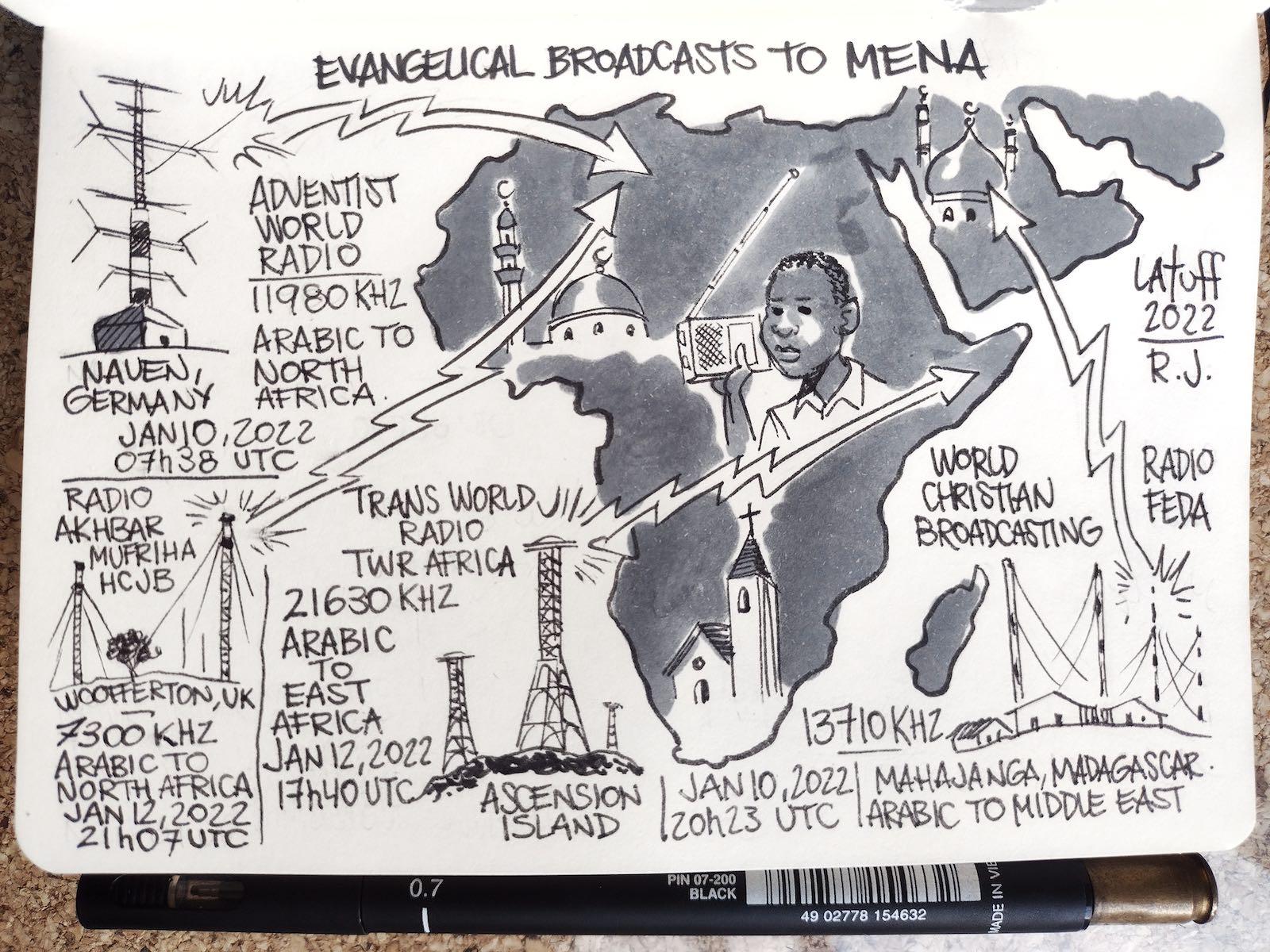
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors NT, Mark Fahey, and @SAKURARadiochan for the following tips:
The RPTF is pleased to announce the launch of La TopoRadio— the best place on the web to explore historical research about Spanish-language radio. La TopoRadio is an interactive map that lets users discover publications about historic and contemporary stations.
The project supports the goal of the RPTF to bring attention to the multifaceted history of radio in the United States. Spanish-language broadcasters have been part of the nation’s heritage since the dawn of the radio era, but this history is often sidelined in official accounts of radio history. Spanish-language programs continue to grow in popularity and geographic reach even while English-language listenership has declined. [Continue reading at the RPTF website…]
Note: the following was copied from the newsletter of Australian radio retailer, Tecsun Radios Australia.
A controversial decision in 2017 lead to the ABC turning off its domestic shortwave radio service, much to the disappointment and anger of remote listeners. It’s reasoning for turning off the shortwave broadcasts was that it would only affect a small number of listeners and in fact save operating costs of $1.9M, which could be re-invested in providing infrastructure of digital services located in populated regional areas.
Many industry groups were outraged, particularly in remote areas of the Northern Territory where residents had come to rely on the service as their only regular source of news and entertainment.
In February 2011, cyclone Yasi crossed the Australian east coast between Cairns and Townsville, causing enormous damage and knocking out all local communications.
Radio Australia carried ABC Queensland coverage of the storm, which was extraordinary.
[…]The federal Labour party has announced that if elected next year, they will provide the ABC with $2M in funding to re-establish the shortwave funding across the territory. [Continue reading…]
The Malahit DDC is the latest in portable SDR packages coming out of the Russian designer and manufacturer known as ‘Malahiteam’. In the past they released the hugely successfull Malhit-DSP. We want to thank Manuel Lausmann for sending us a video and review that comprehensively looks at one of the first Malahit DDC devices that have been received. Manuel writes:
[…]The comparison took into account the results from the DDC versions with two ADC versions – AD9649 and MDRA1A16FI.
1) the sensitivity is about the same, there is no difference.
2) The dynamic range blocking is a big difference in favor of DDC. It is caused by the properties of the radio reception path and not by the difference in the classes of radio receivers. This has the practical advantage that a radio receiver with large antennas can be used under difficult conditions, for example when it is necessary to receive a weak signal in the presence of a strong interfering one.
3) The dynamic range of third order intermodulation is a big difference in favor of DDC. It is caused by the properties of the radio reception path and not by the difference in the classes of radio receivers. The practical advantage of this is the lack of parasitic or false reception channels. [Click here to read the full article and watch the video at RTL-SDR.com…]
Note that “Cordial Cold War: Cultural Actors in India and the German Democratic Republic” is now free in eBook form on Amazon.com. Here’s the description:
Cordial Cold War examines cultural entanglements, in various forms, between two distant yet interconnected sites of the Cold War—India and the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Focusing on theatre performances, film festivals, newsreels, travel literature, radio broadcasting, cartography and art as sites of engagement, the chapters spotlight spaces of interaction that emerged in spite of, and within, the ambits of Cold War constraints. The inter-disciplinary collection sheds light on the variegated nature of translocal cultural entanglements, at work even before the GDR was officially recognized as a sovereign state by India in 1972. By foregrounding the role of actors, their practices and the sites of their entanglement, the contributions show how creative energies were mobilized to forge zones of friendship, mutual interest and envisioned solidarities.
This volume situates actors from the Global South as mutual co-shapers of the cultural Cold War, therein shifting its Euro-American and Soviet epicenters to Non-Aligned India. Going beyond official state channels of international political dialogue, it locates cordiality in the micro-histories and everyday experiences of interpersonal engagements, bringing to focus a hitherto underexplored chapter of India–Germany entanglements.
Click here to view on Amazon.com.
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!