It’s been a busy winter season here at SWLing Post HQ. Many of you might have noticed a slow response time if you’ve tried to contact me. I’m in the midst of a rather involved investment property renovation that’s consumed nearly all of my spare time.
Still, I’m keeping up with the Post and even managing a little one-on-one radio time in the early mornings/late evenings. Indeed, I’ve actually tried to turn my renovation project into an opportunity to play a little radio. The property is unoccupied and very rural, so there’s quite literally no RFI there. Woot!
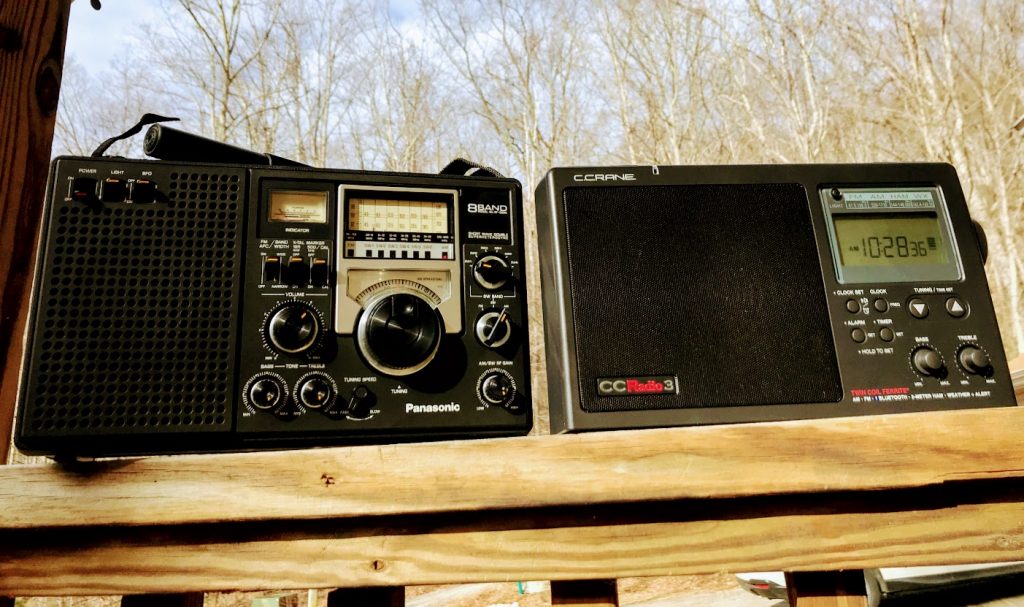

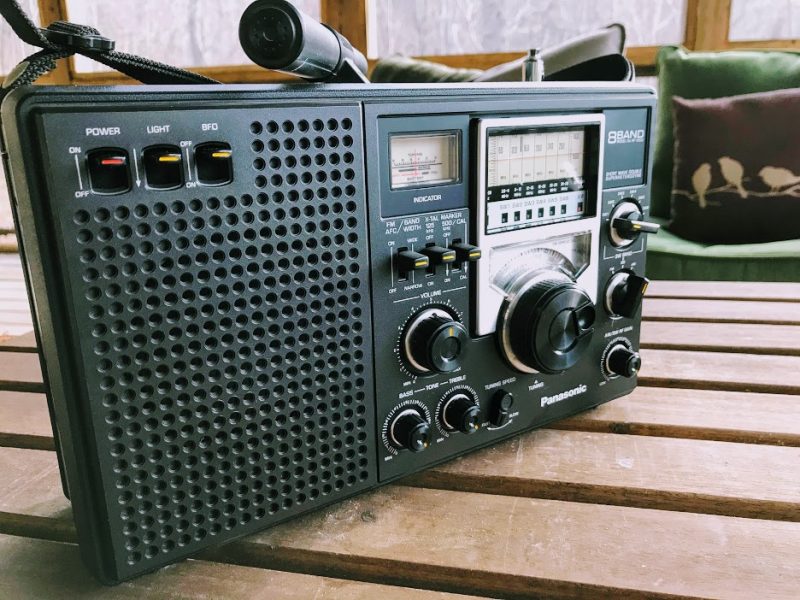
Since I’ve been spending time evaluating the new CCRadio3 (click here to read my preview), I’ve also had the CCRadio EP Pro, Sony ICF-5500W and the legendary Panasonic RF-2200 nearby for comparison purposes.
All of these radios have their strong points, but the Panny RF-2200 is still the rig I reach for the most. That’s why I listed it as one of my daily drivers.
It also helps that my RF-2200 feels like a brand new unit after Vlado re-capped and cleaned it.
Band-scanning
Band-scanning with the RF-2200 is such a tactile experience. The ‘2200 tuning knob is quality and almost feels like a weighted encoder you’d find on a proper tabletop receiver. The RF-2200 even has fast/slow tuning gears and you can calibrate the dial so easily. Though tuning on the shortwaves feels a little vague, I find mediumwave is incredibly accurate.
Speaking of the dial and logging scale, I think it’s one of the most attractive from the 1970s:
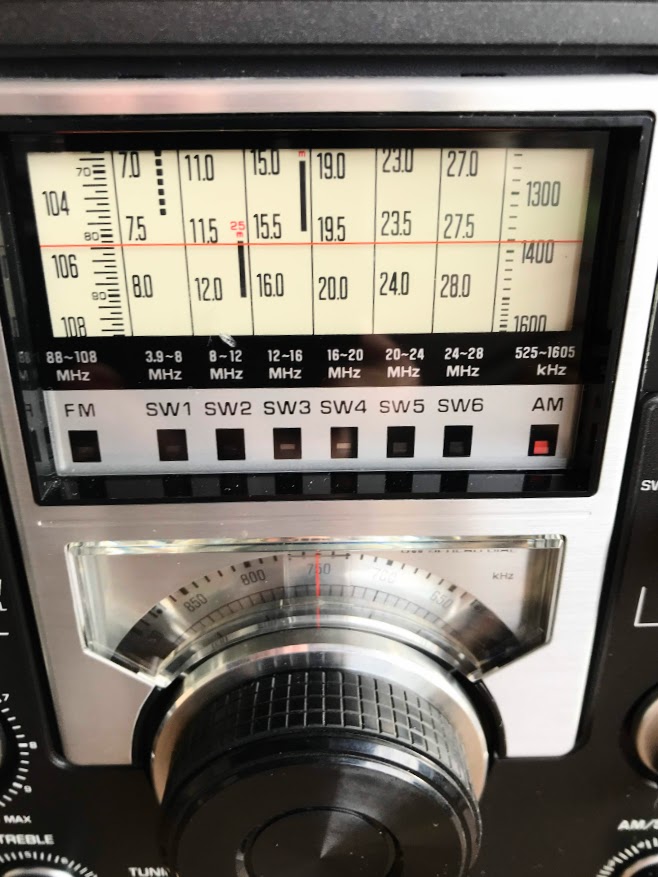

Since I’ve been doing most of my listening around sunrise and sunset, it’s been a lot of fun to fit in a little mediumwave DXing as well. I see why the RF-2200 was one of The Professor‘s favorites.
If you ever find a good deal on a Panasonic RF-2200, don’t hesitate, just grab it! Occasionally you’ll find one on eBay, but also check your local hamfests and swap meets! That’s where I’ve had the most luck.
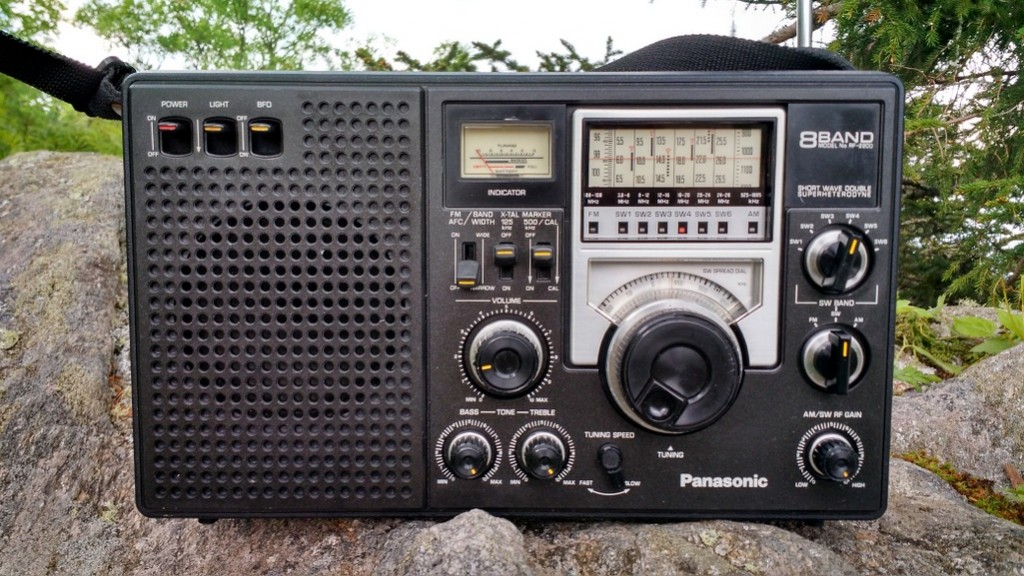

If you ever find a ‘2200 for less that $100-125 that’s in decent cosmetic shape, with the original antenna, clean battery contacts, and is in good mechanical shape (meaning the tuning mechanism and dial work as they should), buy it! If there’s an electrical problem, Vlado can fix that. In fact, if your RF-2200 still has the original capacitors, you’d probably want to re-cap it anyway to keep leaky caps from eventually harming the board or internals. Plus, a properly re-capped ‘2200 will play like a new one!
My takeaway? The RF-2200 is a keeper! I suppose that’s why I even have a spare!
Do you have or would you like an RF-2200? Please comment!
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!