Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, 13dka, who shares the following guest post:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, 13dka, who shares the following guest post:
Dipping my toes into transatlantic MW DX
by 13dka
Most of my SWLing life I wanted to dig into MW DX but never managed to make that really happen for some reason. Then last November, I fetched my first transatlantic station while I wasn’t even trying, in a rather surprising setting:
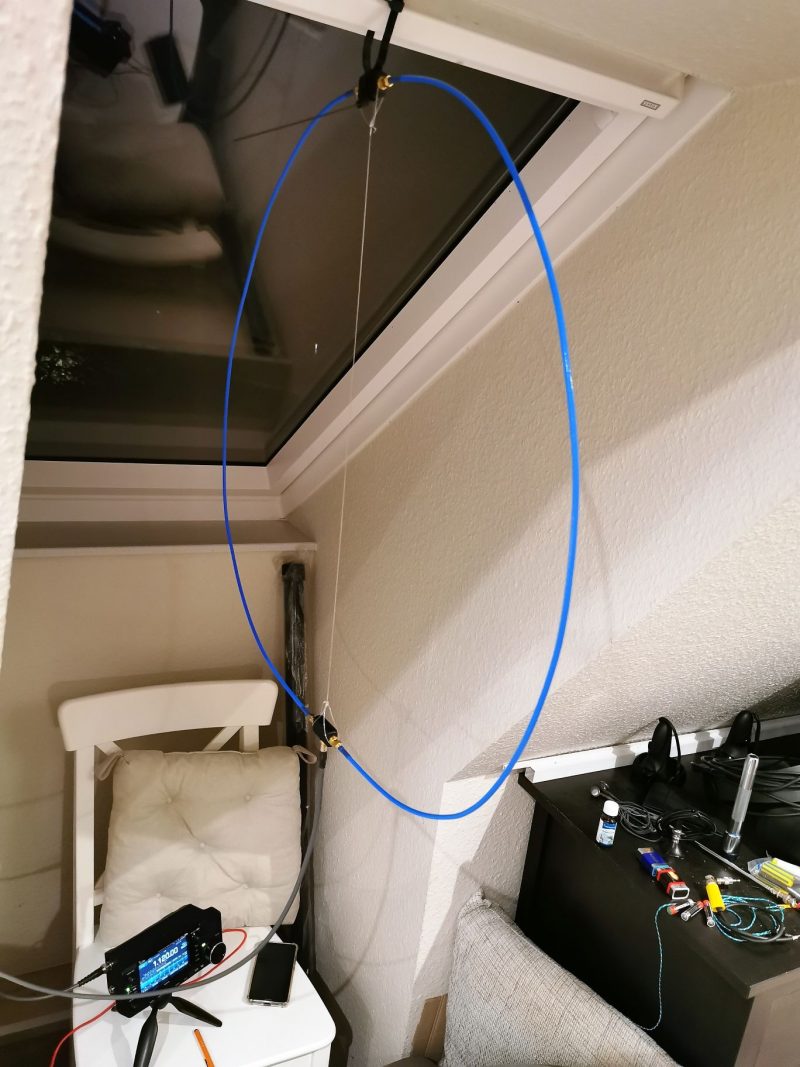
I have to explain that my home and neighborhood got so infested with a multitude of QRM sources that I did not put my outdoor antennas back up after a storm blew them out of the trees in winter 2018/19. I just used an ML-200 loop indoors, which also has to put up with my own additional QRM sources in my den, consisting of 3 computers running 24/7 and a couple of switching power supplies, a TV, LED lighting… allowing for very basic reception as long as my neighbors don’t watch TV or use the internet. On top of that, medium wave is badly beaten by a mowing robot’s boundary wire here, making reception on several portions of the band completely impossible.
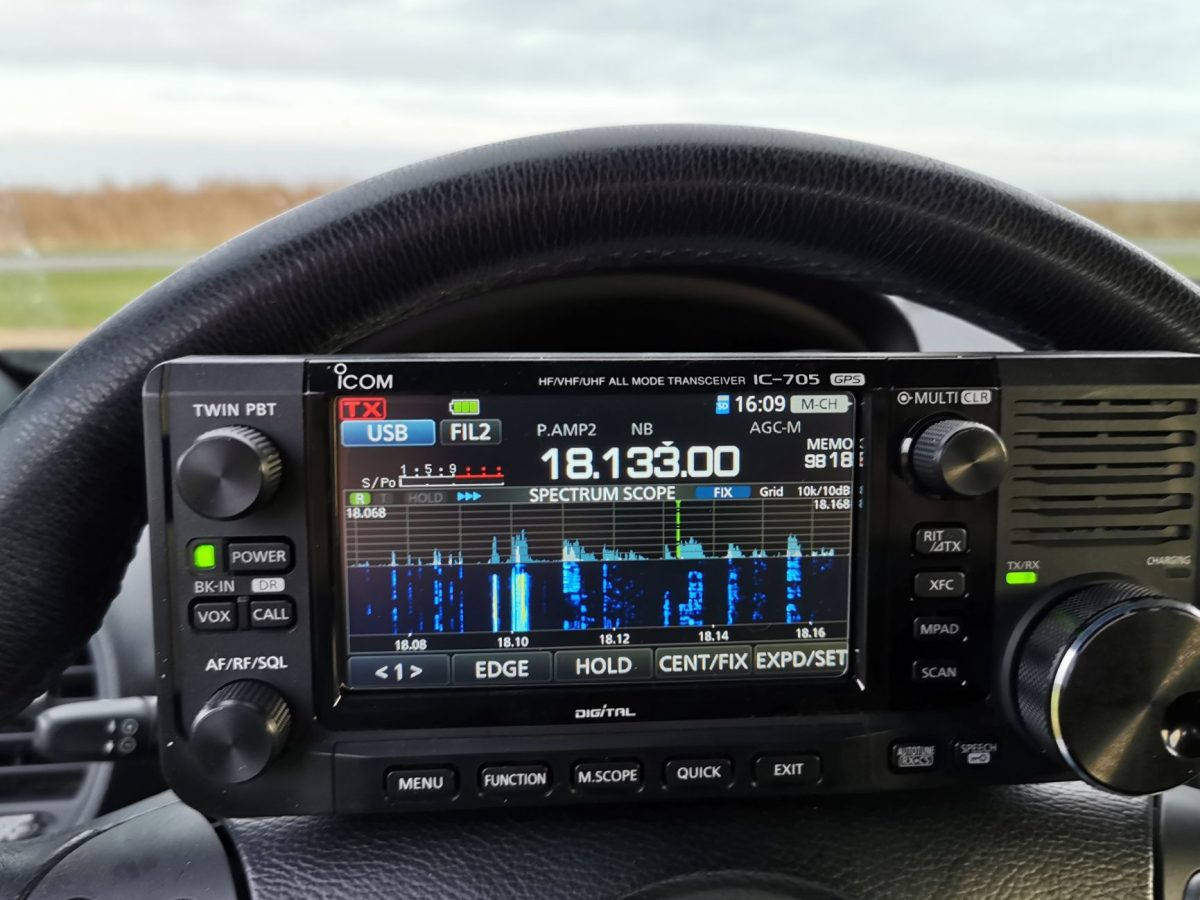
I never expected receiving any US stations on MW in that noise, but I couldn’t sleep that night and scanned the bands a bit with the IC-705 hooked up to my new YouLoop hanging over my bed for testing. I had seen the characteristic transatlantic carriers on MW many times before on my SDRs, but for some reason I never picked up anything intelligible on them in any winter season, now a lot of these carriers were there again but on 1130 there was actually modulation and it wasn’t the only station!
Bloomberg Radio 1130 came in with almost enjoyable quality at times, but Bloomberg is also kind of a surefire station for MW DX over here. I also picked up a station on 1120 and another one on 880 which was briefly so strong that it surmounted the strong interference from BBC Radio Wales on 882 kHz. 1120 was confirmed the next night to be KMOX in St. Louis, 880 kHz was *not* KCBS in NY – I checked that immediately, I have a KiwiSDR set to that frequency booknarked on my cellphone in case I have a craving for the 1-877-Kars-4-Kids commercial. Powerwise likely candidates for that would be CHQT (50kW) in Edmonton, CKLQ (10kW) in Manitoba or KRVN in Nebraska (50kW class B station) but this may be hard to verify due to the dominance of the BBC on that frequency. Anyway, KMOX wasn’t a bad catch for a small, passive indoor loop, that’s 7,150km or 4,440 miles from here!
Bloomberg Radio on the YouLoop:
Here’s KMOX:
This was A) quite encouraging for nighttime DXpeditions to the dike (brrr…cold!), B) a testimony for the YouLoop’s good performance on MW and C) a testimony for the IC-705 having pretty much all one could wish for in a capable MW DX radio – notch filter, passband tuning on AM, stable ECSS, waterfall display to detect stations and last but not least loads of sensitivity to make the most out of low-output antennas down on MW.
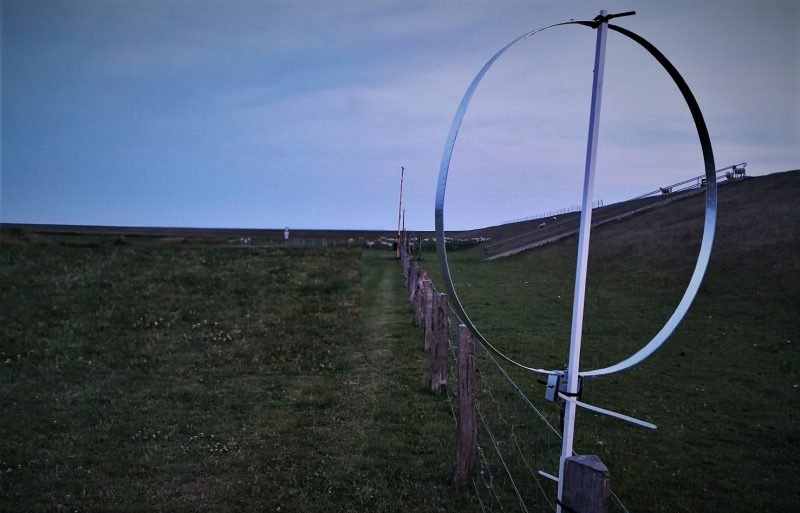
Going to the dike
Of course I just had to put on some long johns and drive to the dike around 3:00am local a few nights later, to try my luck with my ML-200 (lacking a better idea) with an 80cm diameter rigid loop. I was mildly surprised that reception wasn’t that much better than with the YouLoop at home. The overall yield wasn’t exactly outstanding compared to other people’s logs but a lot of stations were hidden in the frequency ranges that are submerged in QRM at home. My log has US/Canadian stations on 20+ different frequencies, unfortunately most of them UNID. Here are some recordings I made that night, hunting for unambiguous station IDs from North American broadcasters:
ML-200, Nov. 16th, 2020
1130 Bloomberg Radio on the ML-200:
Presumedly WABC 770 in NYC: In MW DX, never think you ID’d something properly just because you heard a city name and the frequency has a clear-channel station located there!
This is more unambiguously 1010 WINS in NYC (with a twist described later)
1030 WBZ Boston, MA – the first part of the clip is showing how it sounds when the signal is good, the second part demonstrates how reliably propagation is taking a rest while a station identifies itself.
The grandpa of AM broadcasting, 1020 KDKA:
Moving away from the east coast, this is WHAS 840 in Louisville, KY:
760 WJR Detroit, MI
Here’s a tough one, the religious content I heard with a great signal before doesn’t warrant a proper ID alone, and as per usual the station ID’d while fading out. I could ID this only with a set of big, closed headphones, which is a mandatory accessory for all extreme DX (CHRB 1140 in High River, Alberta):
Of course I was occasionally checking other bands too and got some serviceable signals from Brazil:
Clube do Para on 4885 kHz:
VOA Pinheiro from Belem, Brazil on 4960:
Going to another dike, this time it’s personal!
Time to try something completely different: A ~1,000m/3,000′ straight (and preliminary considered continuous) stretch of mesh fence along the dike heading ~345° (NNW), pointing roughly to mid-/western mainland North America. I had briefly tried its aptitude for being a “natural” Beverage antenna before – with mixed but encouraging results: Due to the fence not being terminated at the far end it may be kind of bidirectional, and according to my latest insights a Beverage style antenna doesn’t work well over very good (conductive) ground, probably even less so close (maybe 200′) to the ocean. Also, I forgot to pack the 9:1 balun I prepared for that purpose, so I just had some wire with alligator clip to connect the fence to the radio. Boo.
Accordingly, what I saw on the waterfall display didn’t look so much different than what I got from the ML-200 before – there were clearly more stations visible (as a carrier line on the waterfall) but nothing was really booming in. However, I managed to log a few more stations, such as WRKO in Boston and (the highlight of the night) 1650 KCNZ “The Fan” in Cedar Falls, IA which has only 1kW to boot at night to make the 6,940 km/4,312 mi to my dike. This may or may not be an indication that the “Beverage sheep fence” isn’t so bad after all!
“Fence”- reception, Nov. 18th, 2020:
VOCM 590, St. Johns, New Foundland, Canada’s easternmost blowtorch is like Bloomberg an indicator station for European MW DXers:
680 WRKO, Boston, MA:
1040 kHz, presumed to be WHO, Des Moines, IA: No ID, only a matching frequency and a commercial for “Jethro BBQ”, which has locations only in and around Des Moines:
Here’s 1650 KCNZ, Cedar Falls, IA with 1KW:
To put that into some relation, this is what 1KW sounds like on a very quiet 40m band in SSB (K1KW from Massachusetts on 7156 kHz producing a 9+20 signal that morning on the “Fence antenna”):
BTW, interesting bycatch – not the first time I caught WWV and WWVH on the same frequency but that morning was the first time I could hear both on 5 MHz:
So where have you been all my life, American AM stations?
A question remains – how could I miss the existence of these stations forever, then in modern SDR times see the carriers on the spectrum scope and still miss the modulation on these carriers? Or the other way around – why did I hear them now?
To begin with, when I started out with the radio hobby many decades ago, the reason for the occasional whine and whistle on some stations (particularly past midnight) wasn’t obvious to me: The last thing I suspected was that this could be interference from across the pond, with the pitch of the whine (or “het”) having a direct relation to the 9kHz vs 10kHz difference in channel spacing. Of course these stations were there all my life! Then, with just some regular radio you’d have to pick one of very few frequencies where a strong station from across the pond coincides with a nice silent gap in the local channel allocation. But until this millennium, European medium waves had no such gaps and a lot more local blowtorches.
Since that time many MW stations were turned off and demolished and whole countries abandoned MW here in Europe, so we’re in a much better spot now for transatlantic DX. Unfortunately the opposite is true for listeners on the left side of the pond, you guys still have a very crowded AM band but less potential DX targets in Europe. On the bright side, the remaining European stations are often not restricted to 50kW and you have another ocean with very distant and rewarding DX stations that are very, very hard to catch in Europe!
Wrong time, wrong place
Another bunch of factors are – of course – propagation, season and location/latitude. The MW DX season is roughly fall to spring nights (when TX and RX are in the dark) with a period of increased absorption in the middle (the “mid-winter anomaly”), signals are potentially stronger at lower latitudes and weaker at higher ones but the distance to the noisy equator and a lack of stations interfering from the N can be a huge advantage for using over-the-pole paths on higher latitudes. The big showstopper is solar activity: Good condx on shortwave can be rather bad for skywave propagation on medium wave, so a solar minimum is the long-term hotspot for (transatlantic) medium wave DX.
I’m glad that I learned how intense that relationship is right away: When I discovered that Bloomberg is pretty good on my indoor YouLoop at home, condx were pretty down with SFI in the low 70s and very little excitement of the auroral zones. 2 weeks later the SFI was only slightly higher in the 80s-100, many of the carriers were missing on the waterfall and Bloomberg could be heard only in much bigger intervals.
Speaking of which – even with favorable condx, a proper radio and a half-proper antenna, patience is key! In my very fresh experience the fading cycles on those over-the-pond signals are long! So far I have seen everything fading in and out over the course of a few minutes to half hours or more, with less favorable conditions or a worse antenna it may take much longer until it sticks out of the noise for a while. So you may have to park on a frequency for a long time to not miss the station coming up so much that it becomes readable at the right time to ID it. Multiple DX stations on the same channel can make identification difficult unless one station really dominates the other and that all may take hours or days until it happens. Here’s a lucky example on 1010 kHz:
Lucky because in this case one station is already known – it’s WINS but it often has another station underneath and I was curious what that station might be. On this occasion, the station ID’d itself as “Newstalk 1010” (which is CFRB in Toronto, 0:05 in the clip) just in a short talking break on WINS. Again, this can’t be heard on my laptop speakers but on headphones:
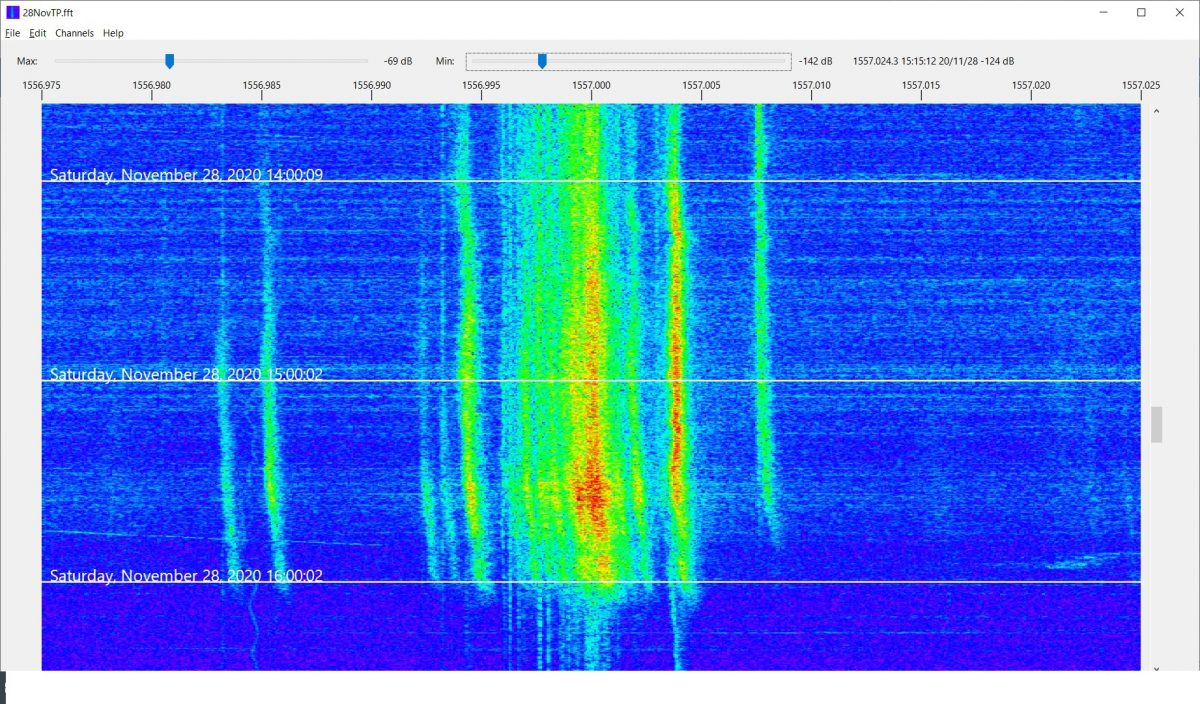
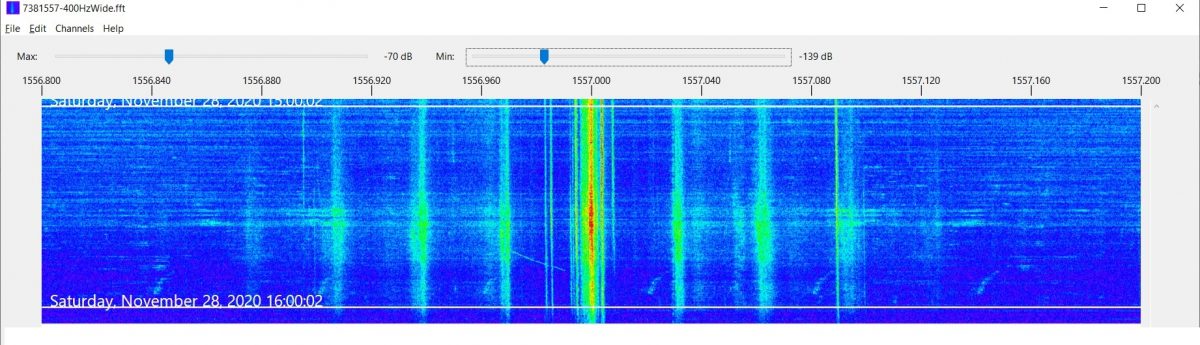
Waiting for a moment like this to happen isn’t exactly fun, that’s why spectrum recordings are incredibly valuable particularly on MW – you won’t miss a possible station ID on frequency A because you were listening to frequency B, but a part of me thinks this is taking a bit of the challenge away, like blast fishing. 🙂
Fancy equipment
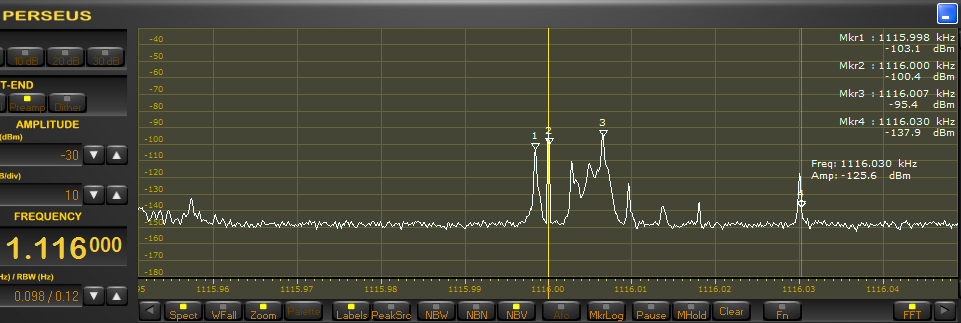
Fun fact: While Bloomberg NY on 1130 was (kind of) booming in at home so I knew for sure it was there, I could hear it even on the XHDAtA D-808 with its tiny loopstick and only average sensitivity on the AM band! So for “easy”, loud and undisturbed stations some persistence and a simple portable radio may suffice to catch some transatlantic DX. But most of the stations will be hit by interference from closer stations, then the radio needs at least to be capable of stable sideband reception, with a corresponding narrow filter and proper suppression of the unwanted sideband – luckily this isn’t an unusual feature on inexpensive portables anymore. So if you already have an SSB capable radio that’s all you need to address the most common issue with transatlantic DX, US and EU stations being too close in frequency. Of course passband tuning and notch filters are most helpful assets in a radio for this, rescuing reception in even more severe interference situations and the spectrum/waterfall display on an SDR helps a lot with finding the carriers and SDRs also have all the nice tools but with some more patience you may find stations with many conventional receivers.
Of course antennas are the crucial component again: If conditions are excellent, even a loopstick may bring the first stations into the log, some small magnetic (wideband) loop could dig up some more stations, from there it’s quickly going a bit esoteric – AFAIK there are no commercial offers for multi-turn (tuned) loop antennas nor are FSL antennas easy to come by, you can’t buy EWE et al antennas either and Beverage antennas for MW are quite a project – not that hard to get a kilometer of wire and there are even kits to buy but it could be much harder to find a place to roll it out in the direction you’re interested in, in an area that doesn’t have electric fences or high voltage power lines within a radius of at least several miles. I guess once you become addicted, you’ll stop asking yourself whether or not it’s worth the effort.
So it’s pretty clear what happened: For catching TA DX stations, the ionospheric conditions must be good, to receive that with a loopstick they must be ideal and that’s what they are currently – it’s winter in what’s still a deep solar minimum and on top of that, some of my radios are very apt for MX DX and I was lucky to listen on the right time on the right frequency. When I started writing this article, my enthusiastic bottom line was supposed to be something like “MW DX isn’t rocket science”, which is certainly true but I think my history with it shows that it’s not exactly trivial either. Maybe that’s why it’s so rewarding, it sure is some hardcore DX challenge that complements the shortwave activity quite nicely and may give you something to look forward to when solar activity is down.