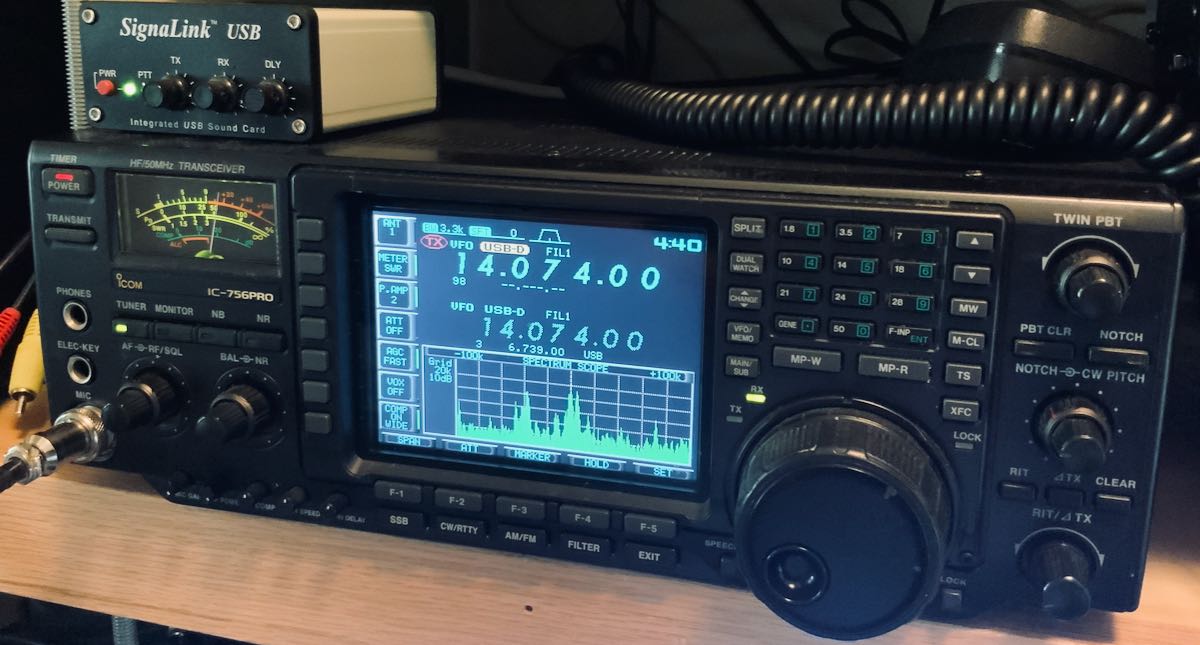
Last year, my friend Matt gave me his Icom IC-756 Pro transceiver.
Last year, my friend Matt gave me his Icom IC-756 Pro transceiver.
Yep, Matt’s a very generous fellow and, trust me, one of the coolest radio guys you’ll ever meet.
Matt was in the process of moving and told me nothing would make him happier than the transceiver to go to a good home and be put on the air. Although it’s actually rather difficult for me to accept gifts like this, I did so knowing that Matt still has some of the coolest radios on the planet. In other words, I wasn’t accepting his only HF radio!
I brought the IC-756 Pro home, attached a power cord and antenna then put it on the air. I just wanted to check out the rig by getting to know the functions and controls much like I do when a new rig lands on my desk for evaluation and review. Thing is, I didn’t stop tuning around for well over two hours!
The IC-756 Pro reminded me how much I miss some of the larger DX or contest-grade receivers and transceivers I’ve had in my shack–most notably, the Ten-Tec OMNI VI PLUS.
For the past few years, with the exception of radios I test and evaluate, I’ve been operating exclusively from the shack with my Elecraft KX3. The KX3 is a fine rig and the ergonomics are well thought-though, but larger rigs (like the IC-756 Pro (II and III), Elecraft K3s, Kenrwood TS-890s, Yaesu FT-DX101, etc. etc.) have a sizeable front panel space that allows for more controls and a larger display. Evidently, I had been missing that.
There’s a reason why we see larger radios being used on DXpeditions even though cargo capacity is often at a premium: performance aside, spacious front panes and informative displays make it easier for radio ops to make quick adjustments without having to reference a manual. You learn how to manipulate the notch, filters, passband, RF gain, split, etc. and muscle memory takes over.
I’m sure this is why SWL DXers like our friend Dan Robinson still prefer and gravitate to commercial, rack-mounted receivers. (I would, too, if I had the room!)
As for the Icom IC-756 Pro, I’ve got it set up to to be my dedicated SSB and digital modes transceiver. I’ll also plan to play a little CW once I find the quarter inch adapter for my key! I haven’t really tested the ‘756 Pro’s performance on the broadcast bands because I have so many dedicated receivers for SWLing and MW DXing in the shack.
The IC-756 Pro is an oldie, but goodie: a very capable transceiver, and a proud resident of SWLing Post HQ.
Not sure if you’ll read this post, Matt, but thank you once again. I’m truly enjoying this rig!
Post Readers: What’s your favorite “big” rig? Please comment with details!