Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Peter Wilson, for sharing the following guest post and DXpedition report:
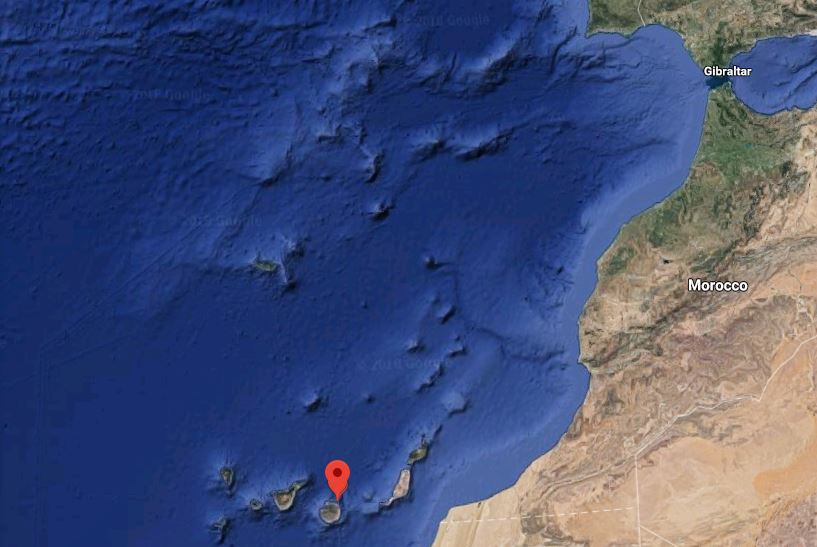
Sony ICF-M780SL MWDX on Gran Canaria
by Peter Wilson
I have spent the last two months in Las Palmas, Gran Canaria adjacent to the Atlantic Ocean.
I travelled light and didn’t bring my radio/SDR collection with me.
A portable I saw in a local department store caught ny eye, and I ended up buying one from a local electronics retailer which had it on special at €55. It is a Sony ICF-M780SL which as turned out, is something rather special. It is a four band (LW, MW, SW,FM) DSP receiver, with an AM IF (LW, MW,SW) of 45 kHz and an FM IF of 128 kHz.
There’s too much hash in my apartment block to use it at home, but as I am a couple of streets away from the Ocean I intended to use it there.
Problem is there almost as much RF hash at the oceanside as at home. Also the Atlantic breakers crash loudly on the shore, and the wind can howl quite loudly. I did have some limited success and have included a couple of clips.
I discovered a better DX location at a small Plaza a short distance inland from the Ocean. There is an early morning peak for MW TA leading up to about 07:30 UTC (= local time)
The radio is used barefoot in each clip. There is some camera hash.
Here are the highlights:
USA Transatlantic
1500 WFED booming with ID 5736 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
790 WAXY with ESPN Radio ID 6369 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
1540 KXEL 6935 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
1530 WCKY 6373 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
770 WABC 5459 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
1520 WWKB
ESPN Radio with sports talk. 5841 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
Ocean front around dusk
1350 TWR Armenia 5377 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
1521 Duba Saudi Arabia 5004 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
1458 Lyca Radio, Brookmans Park UK 2914 km
Click here to view on YouTube.
The Sony ICF-M780SL is a great MW/LW/FM performer. SW propagation has been mediocre and suffers from the RF hash QRN, so difficult to test.
Amazing, Peter! It’s hard for me to believe the reception you had of WFED (Federal News Radio). I listen to that station every time I go through the DC/Baltimore area and I think your reception is just as good. A TA crossing of almost 5,000 km with armchair copy! Quite an accomplishment!
Thank you for sharing your Gran Canaria DX with us. I’m pretty impressed with the Sony ICF-M780SL as well.
Post Readers: make sure you check out Peter’s YouTube channel by clicking here.
Click here to search Amazon.co.uk and click here to search eBay for the Sony ICF-M780SL.