This article, which extensively reviews–and compares–the Tecsun PL-880, PL-660, the Sangean ATS-909X, and the Sony ICF-SW7600GR, originally appeared in the June 2014 issue of The Spectrum Monitor Magazine. Without a doubt, it’s my longest and most comprehensive review to date.
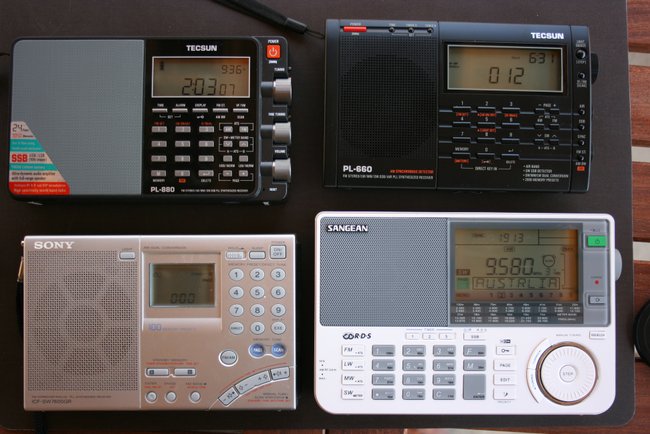

Summer: time for travel–and for portable shortwave DXing. As I mentioned in the March TSM issue, I love combining travel with shortwave radio listening. But what radio should I pack?
This time of year, on the SWLing Post, I receive an increase in the number of queries asking some variation of the following, “What is the best, full-featured, portable shortwave radio on the market?” Oftentime it’s an upcoming trip, or just some time off work, that prompts the question, but without a doubt, this is the most-often-asked question from my readers. Typically, the reader has several models in mind and is curious how they compare. And since a good portable radio costs between $100 – $230 US, it’s not an impulse purchase decision for most of us.
In this month’s column, I hope to answer this question as thoroughly as possible so you can make an informed purchase decision that’s right for you. All four radios I mention in this article are what I would call “flagship portables” (generally, these are the best portables from any particular manufacturer). These were recently featured in a highly-energized reader survey on the SWLing Post, and are as follows: the Tecsun PL-660, the Tecsun PL-880, the Sony ICF-SW7600GR, and the Sangean ATS-909X.

The price tags for these radios fluctuate, but all are generally available between $100-$230 US, and are actively in production right now.
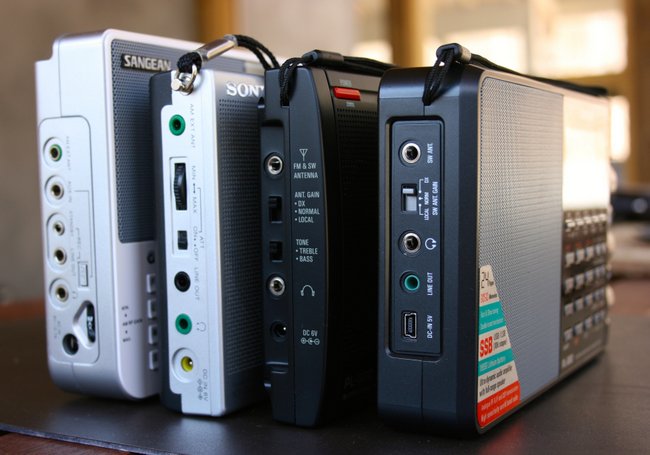
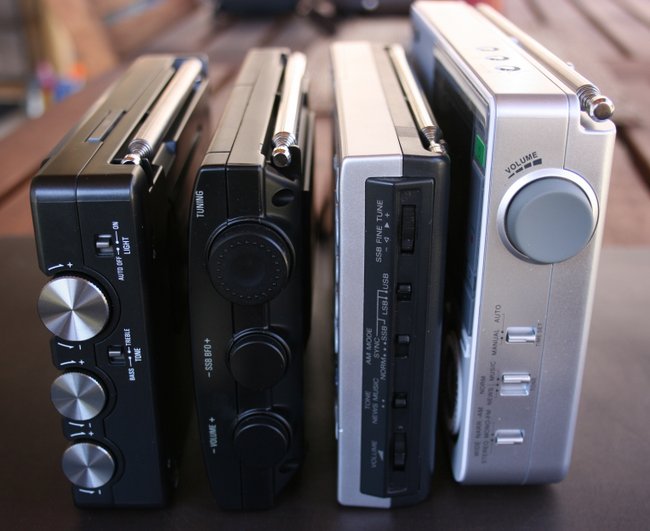
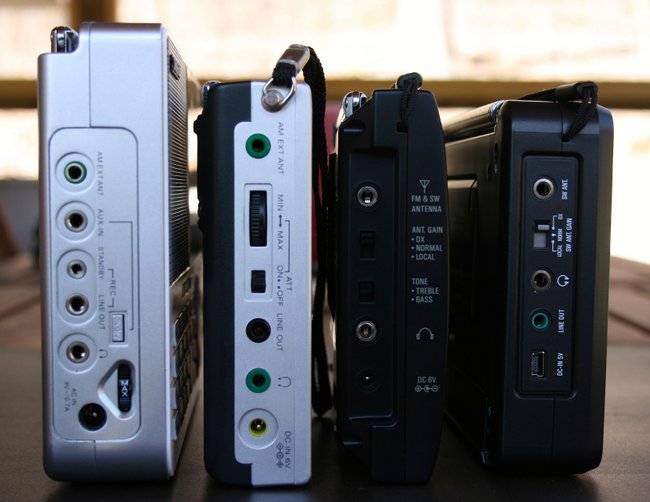
Moreover, all these radios have a similar form factor: they are portable enough to be operated handheld, sport a direct-frequency entry keypad, a dedicated external antenna jack, and a generous backlit display. All of them also have SSB, and all but one have selectable sideband synchronous detection.
The competitors
With the exception of the Sangean ATS-909X–on loan from a friend for the purposes of this review–I have easily spent 40+ hours of listening time with each of these radios. I know their individual characteristics quite well and have used them in a variety of situations.
In case you’re not familiar with each of the contenders, a brief summary of each radio follows with an overview of the features that make it unique.
Sangean ATS-909X
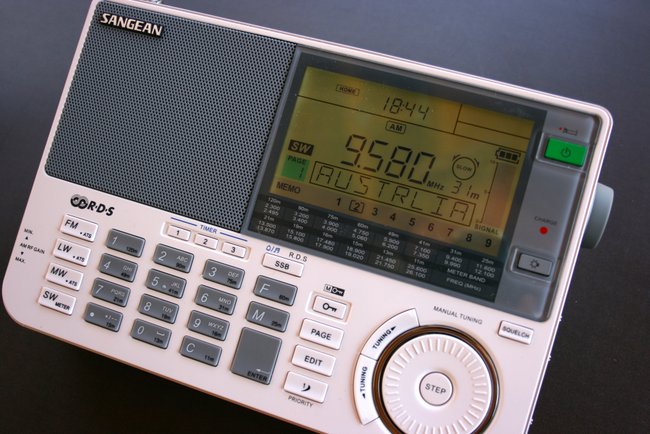

If there was an award for the best-looking radio, I think the ATS-909X would win. The 909X designers put a great deal of thought behind the design and ergonomics of the 909X; for instance, there are two indentations on the back of the radio which allow it to fit nicely in your hands. The 909X sports an internal speaker that produces excellent audio fidelity with a crisp response and even some distinct bass notes, especially notable if listening to an FM station. Of all of the radios listed here, the 909X has the the best variable receiver gain, tone control, largest display, and is the only radio with RDS (Radio Data System).
While I like the position of the tuning wheel on the front of the radio, which is ideal for tuning with your thumb and reminiscent of the ICF-SW55, I don’t like the indents you feel as you tune. If you’re a listener that takes advantage of radio memory, the ATS-909X has a very appealing feature: alpha-numeric memory tags. When you store a Radio Australia frequency to memory, your 909X can display the full station name in large, easy-to-read characters.

There is one omission from the 909X, though, that I find a bit surprising: it has no synchronous detection. While I don’t use a sync detector all of the time, it does come in handy when fading (QSB) and adjacent signal interference (if the sideband is selectable) are present. For a radio that costs over $210 US, on average–the priciest on this list, by a long shot–I feel like sync should have been a given.
Sony ICF-SW7600GR
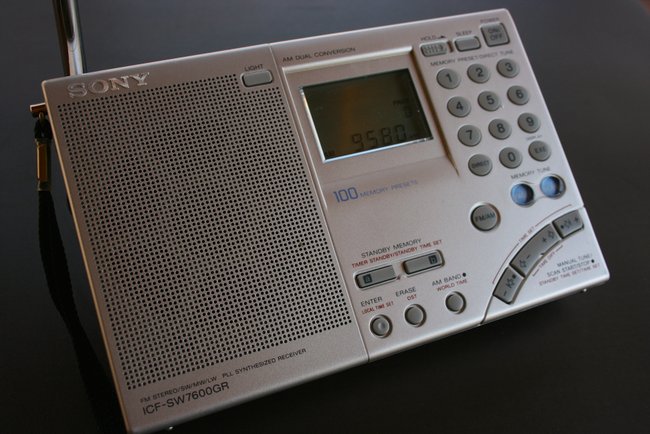

The Sony ICF-SW7600GR comes from a series of “7600” portables that date back to 1977. Though the ’7600GR has all of the modern features one would expect for a radio in its price class, it’s a bare-bones receiver in this particular crowd. It lacks the advance memory functions of the PL-880, PL-660 and, especially, the 909X. The display is smaller and more basic, although it does provide the most vital information.
I have traveled extensively with the ’7600GR, however, as it has rock-solid, reliable performance; it’s my work horse and go-to radio for field recordings because I find its AGC and sync detector remain among the best in this class of radio. It also has a dedicated, stable line-out jack. Important controls are all accessible, and I can easily engage the key lock without fear of accidentally pressing the wrong button during the recording.
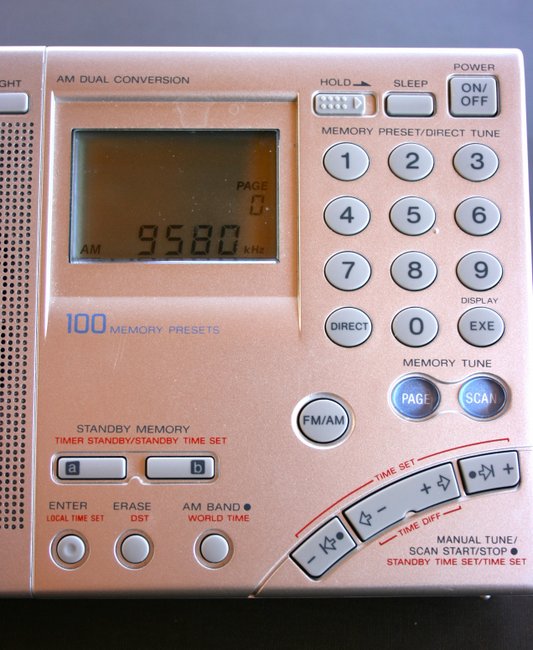

My main gripe about the ’7600GR, however, is its lack of a tuning knob and overall poor ergonomics. My personal preference is to use a tuning knob for band-scanning, as pressing buttons just doesn’t give the same sense of responsiveness. For casual tuning and band-scanning, I leave the ’7600GR in its case. Nor is this radio intuitive–indeed, to learn all but the most obvious functions of the ’7600GR, you’ll need to reference the owner’s manual. Audio from the ’7600’s internal speaker is average/unremarkable.
Still, my Sony ’7600GR’s solidity makes it a friend I would never part with. The real test? If it was ever lost or broken, I would promptly repair or replace this radio.
Tecsun PL-660
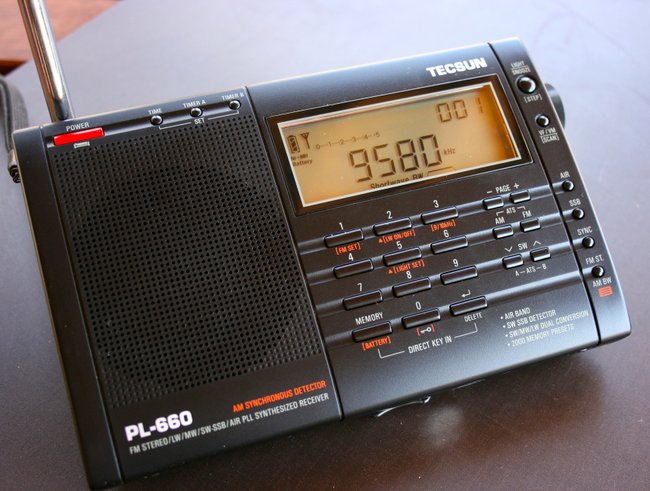

Though I’m often an early adopter of new shortwave portables, I wasn’t for the Tecsun PL-660. When it came out, I figured it would be redundant, considering the many other portables I own with synchronous detection.
Long story short: I was wrong.
Having at last acquired the Tecsun PL-660 last year, I now know it’s a pleasure to operate, and feature-rich for its price. The PL-660 is the bargain in this bunch of benchmark rigs, and significantly so: at an average price of $105 US currently, it is easily half the price of the ATS-909X.
The PL-660 is a pleasure to operate, and a true performer. Its selectable synchronous detector is one of the best in this group of portables: it’s on par with the Sony ICF-SW7600GR. It locks onto a station and rarely loses that lock. Ergonomics are excellent on the PL-660, too–the buttons have a tactile response, are well marked, and all functions are simple to find. The right side-mounted tuning knob has a smooth action.
The Tecsun PL-660 has been on the market since 2011 and has a dedicated following amongst SWLs, many of whom favor it above anything else in its class.
Of course, the PL-660 isn’t perfect, however. It lacks a line-out jack, something I find essential for recording shortwave broadcasts. The audio from the internal speaker is okay, but not on par with the ATS-909X, or its cousin, the PL-880 (below). Still, at $105 US, the PL-660 is truly a steal.
Tecsun PL-880
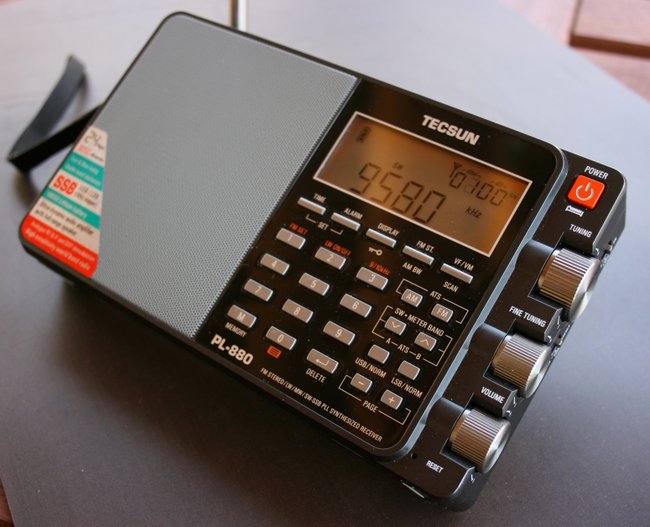

The Tecsun PL-880 only started shipping in November 2013. It was highly anticipated as the new flagship portable in the Tecsun line. The PL-880 is chock-full of features and without a doubt, is the most complicated portable I’ve ever reviewed.
The PL-880 feels like a quality piece of kit: its buttons have a highly-tactile response, the tuning/volume wheels are silky smooth, and feel well-engineered. Out of the four portables evaluated here, I find the PL-880 the most pleasurable to operate. One of my favorite features is its dedicated fine-tuning knob, just below the main tuning knob on the right side of the radio.
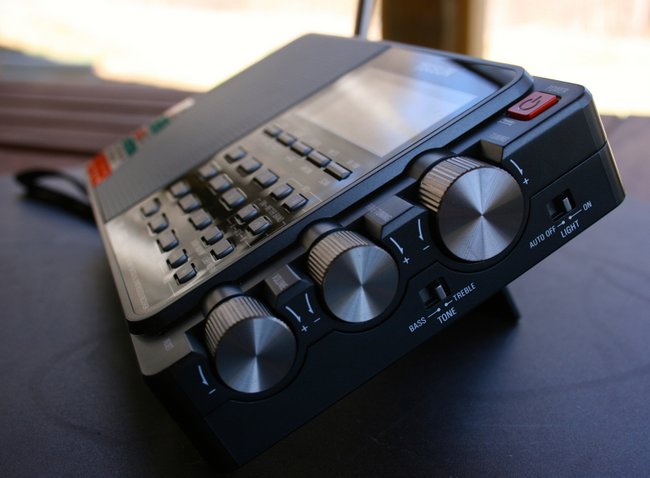

Unquestionably, the one feature which makes the PL-880 highly desirable is the amazing audio fidelity you’ll enjoy from its built-in speaker: it’s well-balanced, rich, and clear. I almost can’t emphasize this point enough–the PL-880’s speaker is capable of room-filling audio. It’s one of the few radios I’ve ever owned (other than some of my antique tube radios) that encourage listening to shortwave from across the room, with pleasing results.
The PL-880 also sports the most filter options of any other portable on the market. Indeed, in SSB mode, the filter can be narrowed all the way down to 500 hz, making this CW operator, at least, quite contented.
Cons? Yes, the PL-880 has some. First of all, I feel like its current firmware version leaves room for improvement. One of the first things I had to do after receiving my radio was adjust the muting threshold so that it wouldn’t engage. Many of the PL-880’s adjustments are mysteriously hidden, even undocumented in the manual. One such hidden feature is its synchronous detection, which is the least refined in this set of portables: it has difficulty maintaining a stable lock, thus audio is significantly compromised.
[Click here for our comprehensive (and growing) list of PL-880 hidden features.]
Changing settings often results in the radio “thinking” for a second or two, during which time it mutes the receiver. This phenomenon is most pronounced when changing modes (from AM to LSB, for example). I find it rather distracting.
Still, I do like the PL-880. Its audio and overall quality make up for any annoyances. I suspect it will have a long product life and a loyal following over the coming years.
Evaluating performance

Since I’m listening to the shortwaves 90% of the time I’m listening to a radio, I’ve limited the scope of my assessment here to the shortwave bands. With that said, none of these radios will disappoint you on AM or FM. I did note in my simple home comparison that the Sangean ATS-909X seemed to be the leader on the FM band. The Tecsuns were perhaps best on the AM (mediumwave) band.
But what about on shortwave? I like using recordings to evaluate shortwave radio performance, typically representative clips that are 25-60 seconds in length. Why? Anytime I have more than two radios to compare, it gets difficult to switch between radios, insuring that I give each one the same opportunity to receive a station. More importantly, with this method, I can listen to the audio clips on my computer, and flip between them quickly to determine characteristics I like in each.
Before recording, I set each radio in the same spot on a table, though I might change the orientation for optimal reception (since this can differ from one radio to another). I then extend the antennas fully and set all of the filters, gain controls, tone, volume levels, and frequencies to the same position on each rig. This way, my comparison can be on an “apples-to-apples” basis.
Note that I do not use an external antenna in any of these tests. This because I believe, when considering portables, they should be able to function very well off of their built-in antennas–thus taking into account situations in which employing an external antenna is not practical.
So that you have an opportunity to evaluate each radio in a “blind” test, I’ll tag each audio sample with a number, the order of which will not necessarily be consistent in each consecutive test. After the clips, I’ll reveal which is which.
Strong Signals

When I evaluate relatively strong broadcasts I typically listen for the best audio fidelity and signal stability a radio can offer. Unless there’s an adjacent signal (and in this case, there was not), I open the filter as widely as possible.
One of the strongest stations in my part of the world is Radio Havana Cuba–not always the cleanest signal, but always at blowtorch power levels. In this sample clip, I tuned our four radios to RHC.
To be fair, propagation from this station was poor the day of recording, so you’ll hear a little fading that is not normally present. Additionally, you’ll want to listen to the full clip, as a portion of each contains RHC interviews that were recorded by telephone (thus “tinnier” sounding); you’ll also hear the typical RHC transmitter hum:
Sample #1
Sample #2
Sample #3
Sample #4
You’ll hear that all of these receivers–with the exception of Sample #3–are nearly identical. Sample #3 is less sensitive than the others, thus more prone to shallow fading and a slightly higher noise level. To my ears, Sample #4 has the best audio quality and receiver characteristics, followed by Sample 2 and Sample 1.
Now let’s reveal the radios behind the samples:
- Sample #1: the Tecsun PL-660
- Sample #2: the Sony ICF-SW7600GR,
- Sample #3: the Sangean ATS-909X, and
- Sample #4: the Tecsun PL-880.
Weak signal DX

I like comparing radios while listening to weak signals and/or when conditions are less favorable. Since I often listen to weak signals (after all, so few broadcasts are actually directed to North America), it’s an important test.
I found a weak signal from Radio Romania International on 11,975 kHz. Normally, the signal would have been much stronger, but propagation was rough and QSB (fading) pronounced at times. Under these conditions, you get the opportunity to hear how the receiver’s AGC circuit handles fading and troughs, how the noise floor sounds as conditions change, and judge the overall sensitivity.
While I give priority to a receiver’s sensitivity and selectivity, there’s obviously more to evaluate here–for example, the more sensitive radio may be less pleasing to the ear.
If you like, jot down what you observe as you listen to each 50 second clip:
Sample #1
Sample #2
Sample #3
Sample #4
Obviously, the radio in Sample #4 is significantly less sensitive than the other radios–it truly struggled to hear the RRI signal under these conditions.
The other radios were able to hear RRI. Sample #3 sounded fine when there was no fading present, but in the fading troughs, there was a pronounced high-pitched noise–most likely a DSP-based noise. Sample #1 had pretty solid copy with stable AGC (automatic gain control). Sample #2 was the most sensitive of this bunch.
Now let’s reveal the radios behind the weak signal samples:
- Sample #1: the Sony ICF-SW7600GR,
- Sample #2: the Tecsun PL-660,
- Sample #3: the Tecsun PL-880, and
- Sample #4: the Sangean ATS-909X.
In this particular test, I was most impressed with the PL-660’s sensitivity, but given the choice, I would have chosen the Sony ICF-SW7600GR as the best overall. Why?
The Sony produced audio simply more pleasant to my ears due to the stability of the AGC.
Wondering if others would draw a similar conclusion, I posted the same clips above on my blog, the SWLing Post (http://wp.me/pn3uc-2pl). I doubted whether many readers would take the time to listen, or to vote, in this blind test. Boy, was I wrong–!
I received about seventy responses by email and in the comments section of my post. All but a very few readers ranked the clips in order of preference. The Sony was the clear favorite, with a total of 40 votes as the best of the bunch. The Tecsun PL-660 was second, with a total of 23 votes as the best. No one voted the PL-880 as best. (Click here for full results: http://wp.me/pn3uc-2qH)
What became very clear from the results and the comments, however, was that people who prefer sensitivity, prefered the PL-660. People who preferred stability, preferred the ’7600GR. In a sense, both were “best,” simply depending on the listener’s preference and/or listening requirements.
Weak single-sideband (SSB)

To test the SSB performance of these radios, I tuned to W1AW as they worked a pile-up from Puerto Rico. You will hear some fading. For those of you not familiar with SSB listening, you should note that W1AW sounds a little “grainy” in all of these recordings; this is simply the audio processor on W1AW’s transceiver which is set to be most audible and punch through the static.
Sample #1
Sample #2
Sample #3
Sample #4
W1AW is barely audible in Sample #1. In Sample #2, audio is well-balanced, with good audio, low noise, and a stable AGC. Sample #3 sounds more narrow (even though its filter, like all, was set to the widest setting), but the audio “pops out” of the static and is very intelligible. Sample #4 sounds much like Sample #2, perhaps slightly more sensitive but with slightly less stable AGC.
By now you may have guessed each radio behind these samples…Here’s the lowdown:
- Sample #1: the Sangean ATS-909X,
- Sample #2: the Sony ICF-SW7600GR,
- Sample #3: the Tecsun PL-880, and
- Sample #4: the Tecsun PL-660.
I believe the Tecsuns perform best in this category, even though the difference between the two models is pretty dramatic. The PL-880 has the best sensitivity in SSB–indeed, I could have probably lowered the gain on my recorder and made the background noise sound even less pronounced, but I wanted the levels to match the other receivers. I was somewhat surprised its 5 kHz filter sounded so narrow on SSB.
The Tecsun PL-660 had the most pleasant audio, but during QSB peaks, its audio would suffer a little distortion (you only hear this once in this sample, near the end of the recording). The Sony had slightly less sensitivity, but the most stable AGC.
Once again, the Sangean ATS-909X struggled to hear the signal, having the least sensitivity of the group.
A note about the Sangean ATS-909X

Alas, the most disappointing radio in all of these tests is the Sangean ATS-909X.
To be fair, however, it’s worth noting that the Sangean performs admirably if connected to an external antenna. Again, I resisted connecting an external antenna in this particular series of tests because I believe a good portable radio’s performance should first be judged upon what it can receive with only its telescoping whip antenna, considering that, when traveling, it’s not always possible to use an external antenna.
Indeed, if you plan to buy a portable that will be hooked up to an external antenna more often than not, the Sangean ATS-909X may be a good choice for you. Its front end can handle external antennas better than most of the radios above (with the Sony as an exception, in my experience).
Syncronous detection
I did not test sync detection, as the Sangean ATS-909X lacks a sync detector and the Tecsun PL-880’s sync detector leaves much to be desired. But many hours of listening to the Sony ’7600GR and the Tecsun PL-660 leads me to conclude that their sync detectors are fairly comparable in performance.
So, how do you translate these results?
Although all of these receivers are considered best in the portable realm for a particular manufacturer, each has a character that suits individual listening skills or requirements.
Herein lies the difficulty offering advice on which portable to purchase. Because radio listening tends to be a solitary hobby, it comes down to personal preference–like choosing a friend. What one person values may matter very little to someone else.
For example, I rarely (if ever) save stations to memory on a permanent basis. Other than temporary auto-tuning memory features, I never give memory functions any weight when making a purchase decision (for myself, that is). Yet there are listeners who place a great deal of emphasis on memory functions.
To be perfectly honest, I think each one of these radios has an individual character that makes it a stand out for a particular type of listening. While I often sort through my collection to give away radios that I seldom use, you won’t find me letting go of any of these rigs. The Sony ICF-SW7600GR is still my favorite portable for field recordings; its stable nature and robust front end mean that I can hook up long wire antennas if I wish. The PL-880 is the radio I reach for if want robust sound and armchair listening to shortwave and mediumwave–I also find it the best of the bunch to tune, a quality machine harkening back to the glory days of Panasonic and Sony. The PL-660 is my simple, bullet-proof performer–when in doubt of conditions, it’s the radio I reach for. If I owned the Sangean ATS-909X, it would probably become my bedside shortwave; its audio fidelity, large display, stable back stand, and ability to benefit from an external antenna make it very appealing for this purpose.
You can’t go wrong with any of these benchmark performers, so long as you know its weaknesses and strengths–which I hope this review has made clear.
If I had to choose just one of these radios…

I’m forcing myself answer this question. While it’s difficult to answer, I believe if I could only have one of these radios for travel…I would chose the Tecsun PL-660. I find it the best overall performer, and a true bargain at its price point.
To be clear, if the Sony ICF-SW7600GR only had a tuning knob, it would be my choice, instead. If the Tecsun PL-880 handled weak broadcast signals better, it might be my choice.
But this is my personal choice; you might have a completely different answer. I guess that’s the point I made earlier–it all depends on the listener.
Now…which do you choose?






















