On Tuesday I received the new CountyComm GP5/SSB portable shortwave radio, a sample sent me from CountyComm. If you’re familiar with the current shortwave portable landscape, then you’ll quickly note that the GP5/SSB shares a striking resemblance to both the GP5/DSP and the Tecsun PL-360. While I hadn’t anticipated writing yet another radio article before the end of the year, having just published a lengthy review of the CC Skywave, my curiosity got the best of me…and before I knew it, I’d spent a few hours listening to and making notes about the CountyComm GP5/SSB as I put it through its paces. In the end, I found I had the makings of a review.
On Tuesday I received the new CountyComm GP5/SSB portable shortwave radio, a sample sent me from CountyComm. If you’re familiar with the current shortwave portable landscape, then you’ll quickly note that the GP5/SSB shares a striking resemblance to both the GP5/DSP and the Tecsun PL-360. While I hadn’t anticipated writing yet another radio article before the end of the year, having just published a lengthy review of the CC Skywave, my curiosity got the best of me…and before I knew it, I’d spent a few hours listening to and making notes about the CountyComm GP5/SSB as I put it through its paces. In the end, I found I had the makings of a review.
Who is CountyComm?
Unlike most other brands I review, CountyComm has only one or two shortwave radio offerings. I wanted to know a little of the back story and motivation behind creating the GP5/SSB, so I contacted CountyComm directly and spoke with their representative, Nick.
Nick explained that CountyComm is a retail distributor of products created primarily for US government use. In a sense, CountyComm is the consumer spill-over from the thousands of products intended, for example, for state and federal agencies.
According to CountyComm, the GP5/SSB is a case in point. The company received a large order from a US government department for an “inexpensive, small portable, AM/FM/SW radio with SSB” for emergency supply caches and diplomatic posts. The GP5/DSP (a.k.a., Tecsun PL-360) fit the bill, but lacked SSB. The request was large enough that CountyComm approached SiLabs–manufacturer of the DSP chip in many of the portables on the market–and asked for help. SiLabs made some design changes and worked directly with the factory in China to produce the GP5/SSB.

The GP5/SSB comes with a medium wave bar antenna, carry pouch, stereo ear buds, wire antenna and manual.
Besides SSB, another interesting design CountyComm implemented was extending the upper frequency range of the GP5/SSB to 29,999 kHz; previous and similar Tecsun models only had an upper limit of 21,950 kHz.
You may note that as of today, there are no similar Tecsun portables on the market–this is because the first batch of units were designed for (and all purchased by) CountyComm. However, I have already heard rumblings that there will soon be a Tecsun PL-365 on the market–if so, no doubt it will turn out to be the GP5/SSB.
First impressions
 Appearance-wise, the GP5/SSB is nearly identical to its predecessor, the GP5/DSP or Tecsun PL-360. The vertical form factor is rather unique in the ultra-portable world, this radio is designed for one-handed operation, much like a handy-talky. The volume and tuning controls are on the right side of the radio and are designed to be operated by thumb (for right-handed operators, at any rate). All of the buttons on the front face are easily operated by your thumb–they’re small, but have a firm response. The GP5/DSP (like its predecessor) lacks a back stand, but does have a belt clip.
Appearance-wise, the GP5/SSB is nearly identical to its predecessor, the GP5/DSP or Tecsun PL-360. The vertical form factor is rather unique in the ultra-portable world, this radio is designed for one-handed operation, much like a handy-talky. The volume and tuning controls are on the right side of the radio and are designed to be operated by thumb (for right-handed operators, at any rate). All of the buttons on the front face are easily operated by your thumb–they’re small, but have a firm response. The GP5/DSP (like its predecessor) lacks a back stand, but does have a belt clip.
The small internal speaker produces clear audio, but sounds a little tinny; there is not even a hint of bass. Via headphones, the audio quality is far better.
Besides a slight modification to the keypad layout to accommodate the new addition of SSB and a bright green antenna tip, the radio is identical to the GP5/DSP and Tecsun PL-360.
FM Performance
The CountyComm GP5/SSB, like many other SiLabs-based receivers we review, has excellent FM sensitivity.
Medium Wave (AM broadcast band) Performance
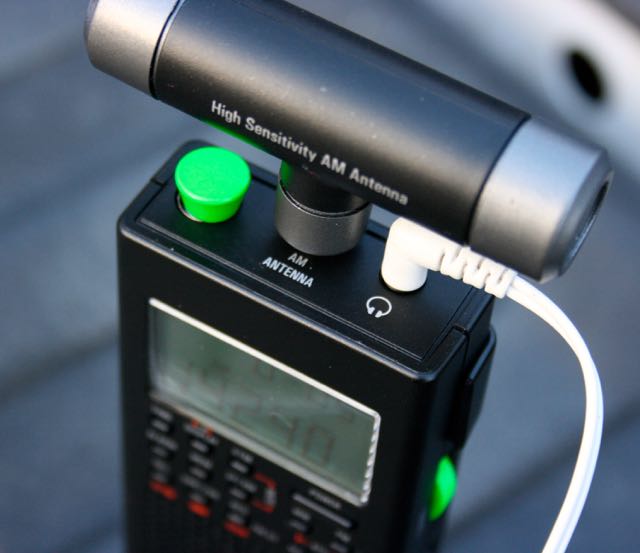

The MW bar antenna increases performance–if using headphones, you will need a right angle connector to allow the MW antenna to rotate 360 degrees
While I have not yet had the opportunity to do a proper comp recording session with the CountyComm GP5/SSB versus comparable radios, I plan to do so in the near future…stay tuned for that, right here! I’ll create a post to give you a heads-up when I’ve added medium wave samples to this review.
With that said, I expect the GP5/SSB performance on medium wave will be very similar to that of the GP5/DSP and Tecsun PL-360. I like the included rotatable ferrite bar antenna that plugs into an external antenna port on top of the radio. It certainly helps with both overall sensitivity as well as nullifying unwanted signals.
Shortwave performance
I’ve had a couple of opportunities to compare the GP5/SSB with other portables on the shortwave bands; embedded audio samples follow of a strong station, a weaker station, and even an SSB sample. Note that all of the sample recordings were taken during poor band conditions–QSB (fading) is pronounced.
Single-sideband
Of course, when I received the GP5/SSB, the first thing I did was tune the ham radio bands in SSB mode.
Nick, the CountyComm rep in charge of the GP5/SSB design, is an amateur radio operator, and I’m pleased that he represented the importance of a truly functional SSB mode on this radio.
 The GP5/DSP only has 1 kHz tuning steps: more than adequate for broadcast listening, but too coarse for SSB. Amateur radio operators do not necessarily transmit right on a frequency; they’re often slightly off-frequency, either accidentally or intentionally. And older ham radios are also prone to drifting until the rigs have properly warmed up. Radios with SSB need finer-tuning controls to hone in on SSB signals. But the GP5/SSB has a work-around for this.
The GP5/DSP only has 1 kHz tuning steps: more than adequate for broadcast listening, but too coarse for SSB. Amateur radio operators do not necessarily transmit right on a frequency; they’re often slightly off-frequency, either accidentally or intentionally. And older ham radios are also prone to drifting until the rigs have properly warmed up. Radios with SSB need finer-tuning controls to hone in on SSB signals. But the GP5/SSB has a work-around for this.
The GP5/SSB accommodates SSB by allowing the listener to select either the upper or lower sideband, then use the BFO function to help fine tune and zero-beat a signal.
Specifically, here’s how to tune to an SSB (phone) amateur radio signal with the GP5/SSB:
- Turn on either the upper or lower sideband, depending on the meter band (generally, 40 meters and below are lower; all else, upper).
- When you hear a signal, use the 1 kHz tuning increments to find where it’s strongest.
- Now, press the BFO button once to activate BFO tuning; the U or L (indicating upper or lower) will begin to blink.
- While the sideband indicator is blinking, use the tuning wheel to adjust the BFO. Adjust tuning until the voices in the signal sound natural.
Once you’ve done this a couple of times, the process becomes second nature.
Overall, I’m very pleased with the SSB functionality and performance. While I prefer either very fine tuning increments, or a separate BFO knob (no room for that on this tiny radio), I appreciate that CountyComm has used the BFO function to eliminate the need for a separate tuning wheel.
Audio samples
While there are a number of portable radios with SSB on the market, there are very few in this $80 price range with SSB. Indeed, to my knowledge there are no other SSB-capable portables currently on the market that are as compact as the CountyComm GP5/SSB.
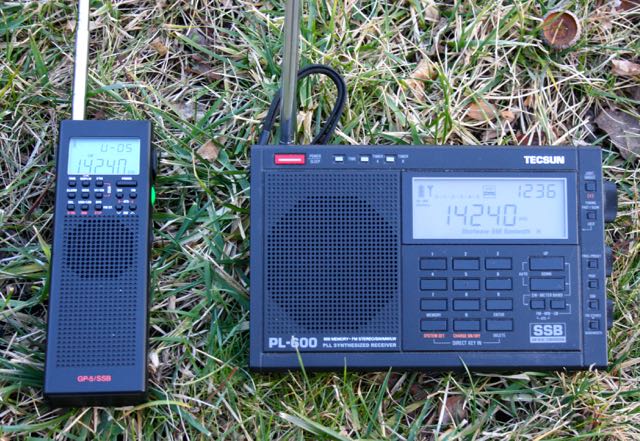
I decided the best comparison radio would be one with a similar price, thus I used the Tecsun PL-600, which (at time of posting) is readily available from Amazon for the same $80 price tag as the GP5/SSB.
Below, you can hear two representative audio samples of how each radio receives an SSB conversation between two ham radio operators on the 20 meter band. I like this sample because one of the operators has a very strong signal, while the other is much weaker:
You may notice that the GP5/SSB has a slightly higher noise floor and DSP artifacts while listening to the weaker signal. The PL-600 sounds a little muffled in comparison.
I listened to many SSB signals that afternoon on the 20 and 40 meter ham radio bands. At length I concluded that I prefer the PL-600 for weak-signal listening. The PL-600’s AGC could cope with the QSB better than the GP5/SSB.
With the majority of the SSB signals, however, I found that the GP5/SSB’s audio was clearer and voices seemed to “pop” out better than on the PL-600.
I should note that I also attempted to include the Grundig G6 in this comparison, but the G6 somehow picked up noise from my digital recorder, thus making the recorded audio sound worse than it actually was. To my ear, the Grundig G6’s SSB reception was very similar to that of the CountyComm GP5/SSB–the G6 perhaps has a very slight edge in terms of weak-signal reception.
Shortwave broadcast listening (AM)
Wednesday afternoon, I had the good fortune to tune in a relatively loud broadcast on 9620 kHz–turns out, it was Radio Nacional de España–! (This is a new shortwave relay service intended to replace the Radio Exterior de España (REE) service that ended in October 2014).
I still had the PL-600 hooked up to my digital recorder at that time; here’s the comparison:
CountyComm GP5/SSB on 9620 kHz
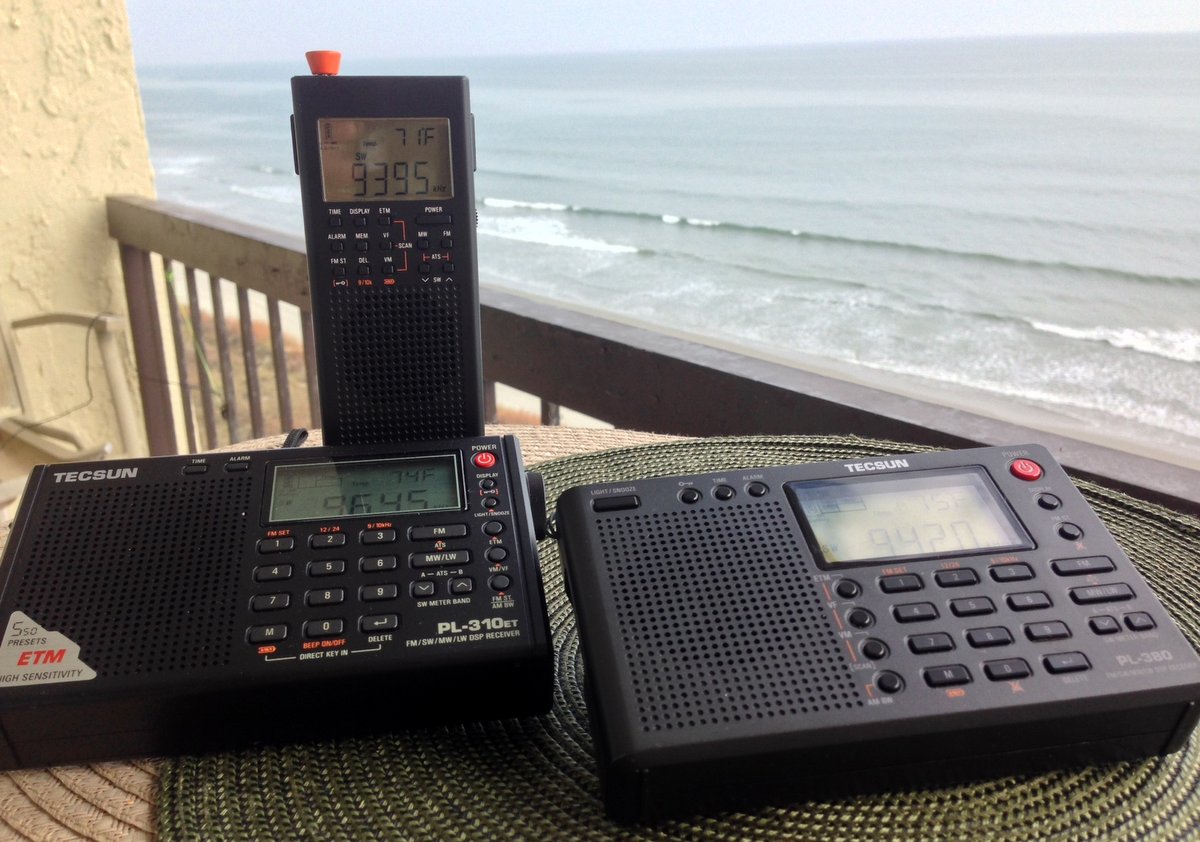
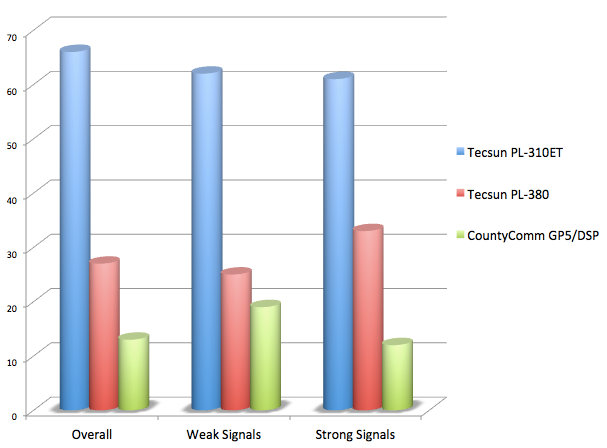
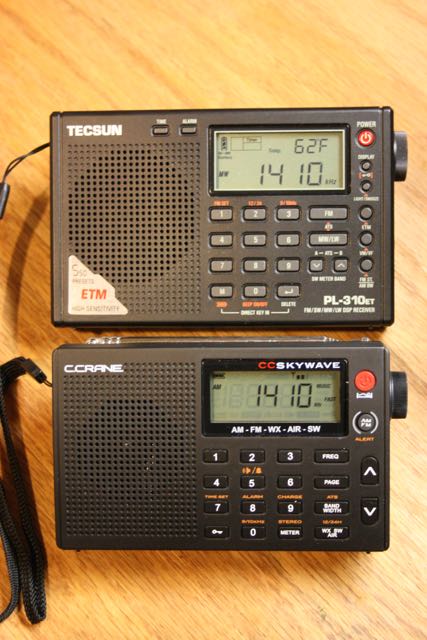
This morning I also had an opportunity to record Radio Australia on 12,065 kHz. This time, I had the Tecsun PL-310ET handy, so I used it for comparison:
CountyComm GP5/SSB on 12,065 kHz
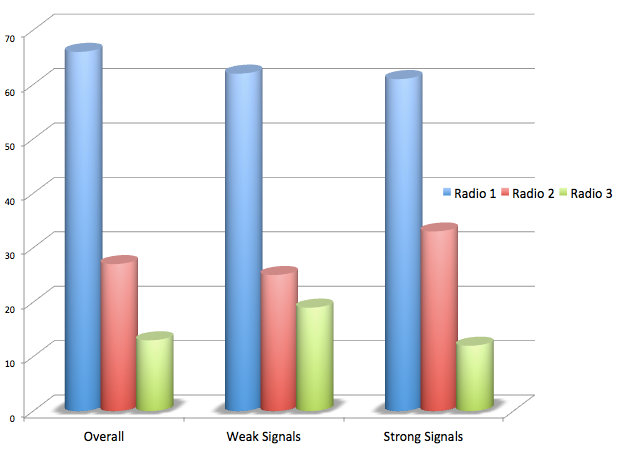
As you probably hear in these examples, the GP5/SSB has fine sensitivity, though not quite as good as the PL-310ET.
I’ve also noted good selectivity during casual broadcast listening with the GP5/SSB.
However, I do not like the GP5/SSB’s AGC (auto gain control) as well as that of the other portables in this comparison–it’s a little too reactive to fading on the broadcast bands. To be fair, these audio samples really accentuated the AGC on the GP5/SSB since all were made during poor reception conditions and pronounced fading.
Under normal conditions, I believe I would be quite pleased with the GP5/SSB; it’s otherwise on par with most of the other ultra-portables on the market.
Summary
Every radio has pros and cons, and I jot down my reactions as I evaluate a new radio so as not to forget any details. The following is my list:
Pros:
- Audio well-tailored for AM broadcast listening–fidelity quite good via headphones
- Adequate sensitivity and selectivity
- Clear, simple LCD back-lit display
- SSB mode is quite functional
- BFO feature allows for zero-beat tuning
- Includes both upper and lower sideband selection
- Much like the PL-880, when in SSB mode, the GP5/SSB will select ham bands when changing meter bands
- Extended frequency range (up to 29,999 kHz)
- Very good medium wave reception with supplied external bar antenna
- Uses three standard AA batteries
- Can be charged with common mini USB adapter
- Displays temperature in Fahrenheit (if MW set to 10kHz steps) or Celcius (if set to 9 kHz steps)
- Great radio for an emergency kit or bug-out bag
- Designed for one-hand operation/included belt clip (see con)
- US Warranty
Cons:
- AGC doesn’t cope with fading as well as other comparable portables
- Audio from internal speaker rather tinny (without headphones)
- No back stand, nor rotatable whip antenna; thus this radio is not ideal for tabletop listening (see pro)
- Supplied belt clip feels flimsy, if you plan to use this in the field, consider purchasing the excellent CountyComm GP5 series rugged case.
Who should purchase the GP5/SSB?
 If you’re looking for an ultra-portable radio for travel and general broadcast listening, I would encourage you to consider the new C. Crane CC Skywave, the Tecsun PL-310ET or the Tecsun PL-380. Overall, the performance and form factor of these radios are a better fit for broadcast listening. If you’re looking for armchair SSB listening, a larger portable with a larger internal speaker such as the Tecsun PL-600 is a good choice for the same price as the GP5/SSB.
If you’re looking for an ultra-portable radio for travel and general broadcast listening, I would encourage you to consider the new C. Crane CC Skywave, the Tecsun PL-310ET or the Tecsun PL-380. Overall, the performance and form factor of these radios are a better fit for broadcast listening. If you’re looking for armchair SSB listening, a larger portable with a larger internal speaker such as the Tecsun PL-600 is a good choice for the same price as the GP5/SSB.
If you’re looking for an ultra-portable radio with SSB, then the GP5/SSB is a very good choice (if not the only ultra-portable SSB choice currently on the market). While the SSB performance can’t compare with larger, pricier receivers and ham radio transceivers, it’s very good for $80 US.
If you’re looking for an emergency communications receiver–something to stash in your vehicle, emergency kit or bug-out bag–the CountyComm GP5/SSB is a great choice and value. Indeed, that’s who the GP5/SSB was designed for; that’s why this rig has excellent frequency coverage in all modes, with good sensitivity/selectivity and designed for portable, one-hand operation. In fact, CountyComm has even designed and manufactured (in the USA!) a robust, protective 1000-Denier case for the GP5/SSB. This case makes it very easy to strap the GP5/SSB to your belt or backpack securely.
 In conclusion, the CountyComm GP5/SSB was designed for a specific purpose: to be an emergency communications receiver. It does this job quite well, despite any shortcomings in comparison to other popular shortwave portables, and for this purpose, I can recommend it.
In conclusion, the CountyComm GP5/SSB was designed for a specific purpose: to be an emergency communications receiver. It does this job quite well, despite any shortcomings in comparison to other popular shortwave portables, and for this purpose, I can recommend it.



















 After just one week with it, I’ve already decided to take the CC Skywave along on my travels to see how it performs over time. It will replace my PL-310ET and PL-380 for my
After just one week with it, I’ve already decided to take the CC Skywave along on my travels to see how it performs over time. It will replace my PL-310ET and PL-380 for my 


















 WinRadio Excalibur
WinRadio Excalibur