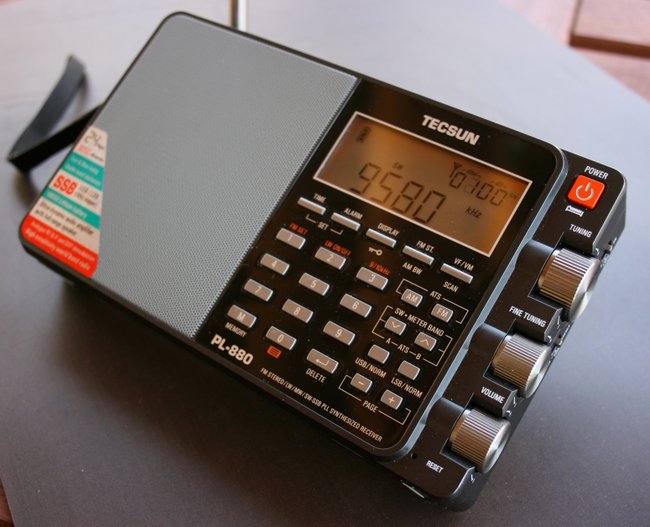
The following review of the CommRadio CR-1 was first published in the August 2013 issue of Monitoring Times magazine.
CommRadio CR-1
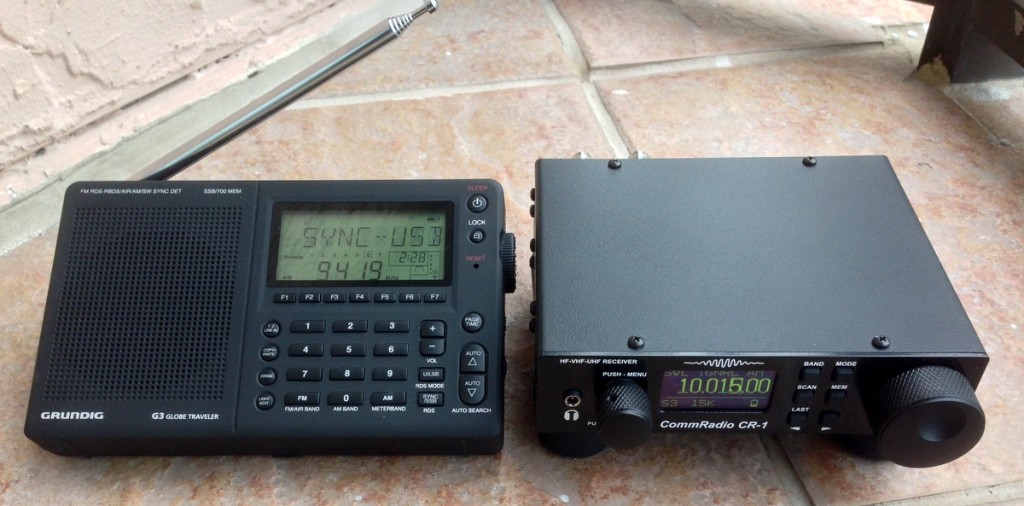
By and large, new products on our radio receiver market these days tend to be SDRs or software-defined radios. And it’s a good thing: by reinterpreting radio digitally, it helps ensure that radio will have a place in this century. Moreover, I’m a big fan of SDRs, as they typically offer a lot of performance for the price. In fact, my main receiver these days is the WinRadio Excalibur SDR. It’s the receiver I use for the bulk of my radio recordings as well as for band scanning.
SDRs often look like a small box with power button, antenna connections, usually computer connections, and, well, that’s about it. Many refer to the SDR as a “little black box.” SDRs don’t require a display; rather, they rely on your PC for this and all other functions.
When I first heard that CommRadio was introducing a new SDR, designed and built in the USA, I expected a similar product, in the form of a small black box. Instead, I encountered a display, tuning knob, volume control, and several front panel buttons; in essence, a small stand-alone self-contained battery-operated SDR tabletop receiver! Needless to say, this was unexpected.
First impressions
When I saw the CR-1 for the first time in person, I was simply amazed by its construction. Being a fan of modest, simple designs, the CR-1 is all that––and, for lack of a better word, “cute.”
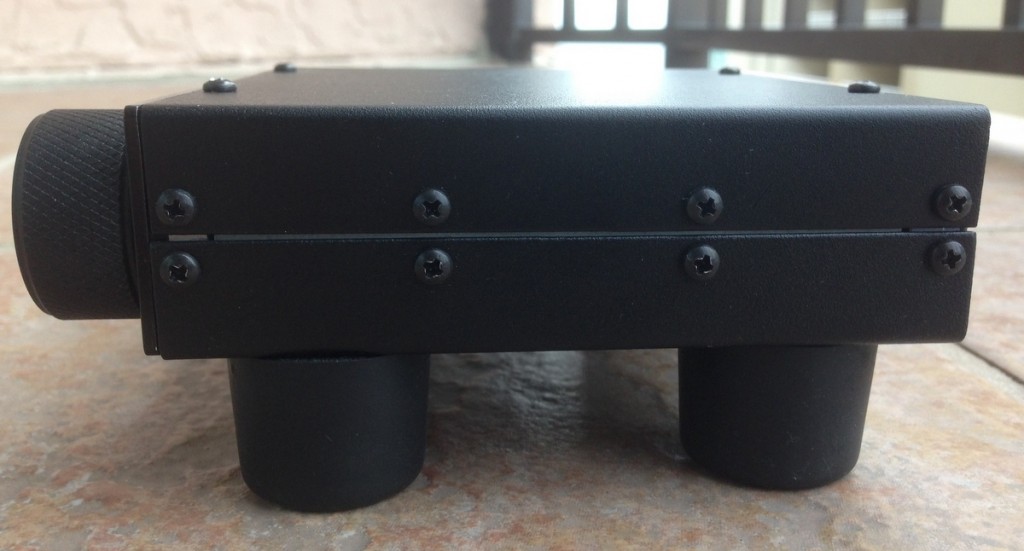
But don’t be fooled by the “cute:” the CR-1 is a very solid product, and a tough one. The case is made of 20 gauge steel, the front panel from machined aluminium, and the tuning knob from black anodized aluminum. Four substantial resin feet lift the CR-1 a full inch, making the height of the controls comfortably accessible, and providing excellent stability while tuning or pressing buttons on the front face.
The OLED display is small–only measuring 1.5” wide by ¾” high–but the resolution is extremely crisp and easy to read, even at a distance or outdoors. All of the relevant information–frequency, filter width, mode, “S” meter–is accommodated by the modest display.
But what about actual operation? Fortunately, I met Don Moore, president of CommRadio, at the 2013 Dayton Hamvention; he kindly arranged to provide a CR-1 for review.
The CommRadio CR-1, I’m happy to report, is a pleasure to operate. I was able to intuit all of the receiver functions without consulting the owner’s manual even once, a major plus.
To turn on the radio, you simply push the volume control knob, the OLED screen displays a “welcome” message, and you’re in business! The CR-1 also defaults to the last used frequency, mode, and filter settings, which is convenient.
There is no numeric keypad for direct frequency entry, only a tuning knob and buttons which allow you to move through the bands. To compensate for a lack of keypad, the CR-1 has a few unique features:
- The tuning knob is adaptive to your tuning speed––the faster you tune the encoder, the more it will increase its tuning steps.
- Tuning to a specific frequency is easy: simply push the tuning knob once to highlight the frequency cursor, then rotate the encoder to reposition the cursor, and press again to lock the position. You can also use the right/left arrow keys to reposition the frequency cursor.
- By setting the automatic tuning mode, the CR-1 will automatically change the mode and tuning steps to coincide with standard band plans.
- You can set the CR-1 to change bands according to the Amateur Radio or Shortwave Broadcast meter band plans.
The tuning knob, while not large, is appropriately sized for the front panel of the receiver. Though not noticeably weighted, a good thing for a small tuning knob, it’s accurate, responsive, comfortable to use for long periods of time, and the finger dimple is perfectly sized for operational ease.
Switching modes is simply a matter of pressing the dedicated MODE button on the front panel of the CR-1, then cycling through options with the right/left arrow keys.
Filters
The CommRadio CR-1 has a good selection of filters which appear to be well-chosen for the appropriate modes. They are as follows:
- CW: 500 Hz, 1.0, 1.8, & 2.6 kHz
- SSB: 1.8 & 2.6 kHz
- AM: 5, 7.5, 15 & 25 kHz
- Non-Broadcast FM 15 & 25 kHz
- FM Broadcast 200 kHz
The DSP filters have typical sharp skirts; I’ve heard no noticeable ringing in CW. Of course, it would have been a nice touch if the filters were variable, still, the existing filters widths are quite effective.
Audio
The CommRadio CR-1 has a bottom-mounted internal 2.5” diameter commercial grade mylar cone speaker; I find that the downward reflecting speaker with a 1” clearance under the radio make for pleasant audio fidelity. Audio out of the speaker is not as robust as I would like, as it lacks bass response, but the audio produced is clear and crisp. I imagine it would produce intelligible audio even in a noisy environment.
The CR-1 also has a port for an external speaker and an internal amplifier that will deliver 0.8 watts into an 8 ohm speaker.
A separate headphone jack is conveniently located on the left side of the CR-1’s front panel. It delivers about 40 mW into 16 ohms–more than enough for the various headphones I’ve tested it with. Audio fidelity is excellent, though I have noticed a faint white noise in my review unit––a detectable high-pitched hiss via my CR-1-connected headphones. It seems to be present at the same low volume even when the volume control is turned down completely; I suspect it may be some noise in the headphone amplifier. The noise does not interfere with listening at all, but audiophiles will certainly notice it. Note: I have reported this to Don Moore, who believes a future firmware revision to the headphone gain chain will fix this.
Performance

Small form factor, multiple antenna connectors, easy grounding and flexible power options (6-18 VDC via standard or USB inputs) make the CR-1 a perfect travel companion.
Shortwave
The CR-1 is an excellent shortwave receiver. How do I know? I know because I pitted it against every HF receiver and transceiver I have on hand (which amounts to quite a few) and it held its own with regards to sensitivity and selectivity. It ran fairly neck-and-neck with my Alinco DX-R8, which is a remarkably good receiver. I imagine it would hold its own against the Icom R75 as well, although it lacks many of the R75’s features. Yet it’s priced well below a new R75.
While the CR-1’s automatic gain control (AGC) copes with weaker signals and selective fading, I would still like to see among its features selectable USB/LSB sync detection. This is a tool I often use to eliminate an encroaching signal on a sideband. I suppose it’s possible that this could be included in a future firmware revision. My Alinco DX-R8 also lacks sync detection, however, so in fairness I can’t say this feature should be expected at this price point.
Mediumwave/Longwave
The CR-1 could receive all of my local AM stations with ease, but weaker stations were more problematic. This could have been a limitation of my large horizontal delta loop antenna; based on the receiver specs, I imagine this would improve greatly with a proper MW antenna. But it’s worth noting that I was using the HF/MW BNC connector on the back, not the higher impedance port for long wire antennas, which might have produced different results.
On longwave, meanwhile, I found I could copy many of our local airport beacons.
VHF/UHF
 As a bonus, the CR-1 provides wideband continuous coverage from 64 – 225 MHz and 438-468 MHZ, covering the FM broadcast band, Aircraft, Marine, Amateur Radio/Public Service, and GMRS/FRS services.
As a bonus, the CR-1 provides wideband continuous coverage from 64 – 225 MHz and 438-468 MHZ, covering the FM broadcast band, Aircraft, Marine, Amateur Radio/Public Service, and GMRS/FRS services.
While I did not spend a great deal of time exploring these portions of the VHF/UHF spectrum, I did find that the CR-1 easily tuned in all my local FM broadcast stations, my local airport tower frequency, and a few amateur repeaters. The squelch control works very well. Note that the CR-1 has a separate UHF/VHF BNC connector on the back panel. In this review, I simply used a telescopic whip with elbow joint to tune through the band––it’s a great portable accessory.
Summary
I took the following review notes of the CommRadio CR-1 from the moment I first turned it on.
Pros
- Wide RX coverage (LW, MW, SW, FM BC/VHF/UHF)
- Good shortwave sensitivity
- Tuning ease (see con)
- Multiple standard antenna connections (VHF/UHF, HF, HF/MW)
- Simple, intuitive operation; barely requires a manual
- Selectable tuning modes (Amateur/Shortwave) adapt modes/steps to band plan
- Well-chosen filter widths, no ringing (see con)
- Small form factor; compact, sturdy design, perfect for travel
- Built-in battery option, with excellent life (as much as 8-10 hours)
- Separate headphone jack (front) and external speaker jack (rear)
- Flexible power source (USB or 6-18 VDC)
- Future updates will include IQ out
- Durable, tough chassis, secure ports, gold-plated circuit board pads
Cons
- No sync detector
- Bandwidth not variable (see pro)
- No direct frequency entry (see pro)
- No noise blanker
- Very slight white noise hiss can be heard over headphones (slated to be fixed with the firmware update)
The CR-1 puts me in mind of a smaller, updated, and more functional Lowe or Palstar receiver; it has a basic, simple design, yet all of the important features you would expect from a receiver in this class. Moreover, it has the distinct advantage of being an SDR; firmware updates can address customer requests, and functionality added––and tweaked––as needed.
While medium wave performance is fairly average, shortwave sensitivity and selectivity are very good, indeed. The CR-1 copes well with both blowtorch stations and weak signal DX. Though my WinRadio Excalibur has a slightly lower noise floor, the CR-1 holds its own at half the cost.
The CommRadio CR-1 might just be the perfect radio for DXers who like to travel. I travel fairly frequently, and I like to travel light. You’ll never see me check in luggage at an airport; my carry-on bag (with radio, of course) is sized to fit in the most restrictive of overhead compartments, like those in many turbo-prop commuter planes. And the CR-1 fits perfectly in my small carry-on. Though I leave them attached, the feet can be removed, thus reducing its size even further. I don’t even worry about extra protection for it, since it’s built like a little tank!
Best yet, since the CR-1 was designed by an aircraft avionics manufacturer, the built-in battery contains less than 1gm of lithium, therefore is well within the limits regulations currently impose. What’s more, should your battery deplete, the CR-1 can be powered by a standard USB connection.
 In short, the CommRadio CR-1 is a fun little radio and in my opinion well worth its ?$500 price. Moreover, functionality may further improve; for example, May 2013 firmware updates included a built-in, functional CW reader and international frequency steps. CommRadio is planning an update later this summer which will produce IQ-out via the headphone jack, and on a date to be determined, we may even see IQ from the USB port. If these are added, the CR-1 will connect to your sound card or USB port, and external SDR application functionality will further expand.
In short, the CommRadio CR-1 is a fun little radio and in my opinion well worth its ?$500 price. Moreover, functionality may further improve; for example, May 2013 firmware updates included a built-in, functional CW reader and international frequency steps. CommRadio is planning an update later this summer which will produce IQ-out via the headphone jack, and on a date to be determined, we may even see IQ from the USB port. If these are added, the CR-1 will connect to your sound card or USB port, and external SDR application functionality will further expand.
The CR-1 has a lot of features––and a lot of potential––in a small, sturdy form, always a good formula for a successful radio. And because of this, even though I currently have a number of portable receivers and transceivers, I will add the CR-1 to my radio collection.
Update: I now own a CommRadio CR-1 and have used it many times while travelling. What I love about the CR-1 is that it gives me tabletop receiver performance in a small, sturdy form factor and can literally operate for hours on a fully-charged internal battery. I have also completed a couple of firmware updates, which are multi-step, though still rather simple. CommRadio has been adding functionality and tweaking performance on the CR-1 since its release, which is most encouraging.
You can purchase a new CommRadio CR-1 directly from CommRadio or Universal Radio.
Update (15 November 2013): Please note that since this review was first published, CommRadio has become a sponsor of the SWLing Post. We thank them for their support!










 “My wife and I live on a boat and plan to go to the Bahamas this season. We cannot afford to install a SSB radio – costs $7K to $8K. But we need to be able to hear the weather reports and forecasts
“My wife and I live on a boat and plan to go to the Bahamas this season. We cannot afford to install a SSB radio – costs $7K to $8K. But we need to be able to hear the weather reports and forecasts






















